Strategies to enhance NK cell function for the treatment of tumors and infections
- PMID: 29953390
- PMCID: PMC6343663
- DOI: 10.1615/CritRevImmunol.2018025248
Strategies to enhance NK cell function for the treatment of tumors and infections
Abstract
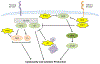
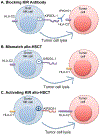
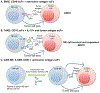
Natural killer (NK) cells are innate immune cells equipped with the ability to rapidly kill stressed cells that are neoplastic or virally infected. These cells are especially important in settings where these stressed cells downregulate MHC class I molecules and evade recognition by cytotoxic T cells. However, the activity of NK cells alone is often suboptimal to fully control tumor growth or to clear viral infections. Thus, the enhancement of NK cell function is necessary to fully harness their antitumor or antiviral potential. In this review, we discuss how NK cell function can be augmented by the modulation of signal transduction pathways, by the manipulation of inhibitory/activating receptors on NK cells, and by cytokine-induced activation. We also discuss how some of these strategies are currently impacting NK cells in the treatment of cancer and infections.
Figures
References
-
- Kiessling R, Klein E, Pross H, Wigzell H. “Natural” killer cells in the mouse. II. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Characteristics of the killer cell. Eur J Immunol. WILEY‐VCH Verlag GmbH; 1975. February;5(2):117–21. - PubMed
-
- Cudkowicz G Genetic control of resistance to allogeneic and xenogeneic bone-marrow grafts in mice. Transplant Proc. 1975. June;7(2):155–9. - PubMed
-
- Karre K, Ljunggren HG, Piontek G, Kiessling R. Selective rejection of H-2-deficient lymphoma variants suggests alternative immune defence strategy. Nature. Nature Publishing Group; 1986. February;319(6055):675–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

