Robotic-arm assisted total knee arthroplasty is associated with improved early functional recovery and reduced time to hospital discharge compared with conventional jig-based total knee arthroplasty: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 29954217
- PMCID: PMC6413767
- DOI: 10.1302/0301-620X.100B7.BJJ-2017-1449.R1
Robotic-arm assisted total knee arthroplasty is associated with improved early functional recovery and reduced time to hospital discharge compared with conventional jig-based total knee arthroplasty: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Aims: The objective of this study was to compare early postoperative functional outcomes and time to hospital discharge between conventional jig-based total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and robotic-arm assisted TKA.
Patients and methods: This prospective cohort study included 40 consecutive patients undergoing conventional jig-based TKA followed by 40 consecutive patients receiving robotic-arm assisted TKA. All surgical procedures were performed by a single surgeon using the medial parapatellar approach with identical implant designs and standardized postoperative inpatient rehabilitation. Inpatient functional outcomes and time to hospital discharge were collected in all study patients.
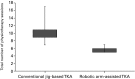
Results: There were no systematic differences in baseline characteristics between the conventional jig-based TKA and robotic-arm assisted TKA treatment groups with respect to age (p = 0.32), gender (p = 0.50), body mass index (p = 0.17), American Society of Anesthesiologists score (p = 0.88), and preoperative haemoglobin level (p = 0.82). Robotic-arm assisted TKA was associated with reduced postoperative pain (p < 0.001), decreased analgesia requirements (p < 0.001), decreased reduction in postoperative haemoglobin levels (p < 0.001), shorter time to straight leg raise (p < 0.001), decreased number of physiotherapy sessions (p < 0.001) and improved maximum knee flexion at discharge (p < 0.001) compared with conventional jig-based TKA. Median time to hospital discharge in robotic-arm assisted TKA was 77 hours (interquartile range (IQR) 74 to 81) compared with 105 hours (IQR 98 to 126) in conventional jig-based TKA (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Robotic-arm assisted TKA was associated with decreased pain, improved early functional recovery and reduced time to hospital discharge compared with conventional jig-based TKA. Cite this article: Bone Joint J 2018;100-B:930-7.
Keywords: Arthroplasty; Hospital discharge; Rehabilitation; Robotics; Knee;.
Figures





References
-
- No authors listed. National Joint Registry for England and Wales. 9th Annual Report, 2012. (date last accessed 22 March 2018).
-
- El Bitar YF, Illingworth KD, Scaife S, Horberg JV, Saleh KJ. Hospital Length of Stay following Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: Data from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample Database. J Arthroplasty 2015;30:1710–1715. - PubMed
-
- Gourin CG, Terris DJHistory of Robotic Surgery. In: Faust RA, ed. Robotics in Surgery: History, Current and Future Applications.New York (NY): Nova Science Publishers, Inc., 2007:3-12.
-
- Cobb J, Henckel J, Gomes P, et al. Hands-on robotic unicompartmental knee replacement: a prospective, randomised controlled study of the acrobot system. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 2006;88-B:188–197. - PubMed
-
- Dunbar NJ, Roche MW, Park BH, et al. Accuracy of dynamic tactile-guided unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2012;27:803–808. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

