Functional role of circular RNAs in cancer development and progression
- PMID: 29954251
- PMCID: PMC6259826
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2018.1486659
Functional role of circular RNAs in cancer development and progression
Abstract
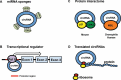
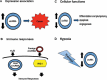
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a large class of endogenously expressed non-coding RNAs formed by covalently closed loops through back-splicing. High throughput sequencing technologies have identified thousands of circRNAs with high sequence conservation and cell type specific expression in eukaryotes. CircRNAs play multiple important roles in cellular physiology functioning as miRNA sponges, transcriptional regulators, RBP binding molecules, templates for protein translation, and immune regulators. In a clinical context, circRNAs expression is correlated with patient's clinicopathological features in cancers including breast, liver, gastric, colorectal, and lung cancer. Additionally, distinct properties of circRNAs, such as high stability, exonuclease resistance, and existence in body fluids, show promising role for circRNAs as molecular biomarkers for tumor diagnosis, non-invasive monitoring, prognosis, and therapeutic intervention. Therefore, it is critical to further understand the molecular mechanism underlying circRNAs interaction in tumors and the recent progress of this RNA species in cancer development. In this review, we provide a detailed description of biological functions, molecular role of circRNAs in different cancers, and its potential role as biomarkers in a clinical context.
Keywords: Circrnas; cancer; carcinogenesis; circRNAs functions; miRNA sponge; tumor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recent progress in circular RNAs in human cancers.Cancer Lett. 2017 Sep 28;404:8-18. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.07.002. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28705773
-
The roles of circRNAs in cancers: Perspectives from molecular functions.Gene. 2021 Jan 30;767:145182. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.145182. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Gene. 2021. PMID: 32991954 Review.
-
Circular RNAs in Embryogenesis and Cell Differentiation With a Focus on Cancer Development.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 May 27;8:389. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00389. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32528957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The understanding of circular RNAs as special triggers in carcinogenesis.Brief Funct Genomics. 2017 Mar 1;16(2):80-86. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elw001. Brief Funct Genomics. 2017. PMID: 26874353 Review.
-
CircRNAs and lung cancer: Biomarkers and master regulators.Life Sci. 2019 Mar 1;220:177-185. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.01.055. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30711537 Review.
Cited by
-
circTLK1 facilitates the proliferation and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma by regulating miR-495-3p/CBL axis.Open Life Sci. 2021 Apr 15;16(1):362-374. doi: 10.1515/biol-2021-0041. eCollection 2021. Open Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33954256 Free PMC article.
-
circ_0038718 promotes colon cancer cell malignant progression via the miR-195-5p/Axin2 signaling axis and also effect Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway.BMC Genomics. 2021 Oct 27;22(1):768. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07880-z. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34706645 Free PMC article.
-
EIF4A3-induced circCCNB1 (hsa_circ_0001495) promotes glioma progression by elevating CCND1 through interacting miR-516b-5p and HuR.Metab Brain Dis. 2022 Mar;37(3):819-833. doi: 10.1007/s11011-021-00899-x. Epub 2022 Jan 17. Metab Brain Dis. 2022. PMID: 35038081
-
Role and mechanism of circ-PRKCI in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Apr 28;25(16):1964-1974. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i16.1964. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31086464 Free PMC article.
-
Alteration in the Expression of Circular Rnas and its association with the Development and Progression of Osteosarcoma, an Integrative Review with High Sensitivity Research.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024 Apr 1;25(4):1195-1203. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.4.1195. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024. PMID: 38679978 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kolakofsky D. Isolation and characterization of Sendai virus DI-RNAs. Cell. 1976;8:547–555. - PubMed
-
- Kos A, Dijkema R, Arnberg AC, et al. The hepatitis delta (delta) virus possesses a circular RNA. Nature. 1986;323:558–560. - PubMed
-
- Hsu MT, Coca-Prados M. Electron microscopic evidence for the circular form of RNA in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1979;280:339–340. - PubMed
-
- Arnberg AC, Vanommen GJB, Grivell LA, et al. Some yeast mitochondrial Rnas are circular. Cell. 1980;19:313–319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
