Acute subclavian artery occlusion with associated clavicle fracture managed with bypass graft alone
- PMID: 29954765
- PMCID: PMC6040510
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2018-224719
Acute subclavian artery occlusion with associated clavicle fracture managed with bypass graft alone
Abstract
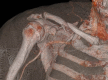
Subclavian artery injury is a rare consequence of clavicle fracture. It most often results from penetrating trauma but can result from blunt trauma with adjacent bone fragments causing rupture, pseudoaneurysm, dissection or thrombosis of the artery. If flow through the subclavian artery is compromised there is a risk of ipsilateral upper limb ischaemia. Life-threatening haemorrhage may result in cases of laceration, and cerebral infarction may result from dissection. Vascular injury in association with clavicle fracture is typically regarded as an indication for internal fixation of the fracture. We present a case of subclavian artery thrombosis in association with a comminuted midshaft clavicle fracture causing limb ischaemia managed by carotid to brachial artery bypass without internal fracture fixation. The fracture united at 4 weeks and there was no sustained vascular or neurological impairment at follow-up. We advocate urgent vascular intervention in subclavian artery injury. There is little discussion in the literature regarding non-operative management of clavicle fractures with subclavian artery injury. We suggest that select clavicle fractures with subclavian artery injury can be safely managed non-operatively.
Keywords: orthopaedics; trauma; vascular surgery.
© BMJ Publishing Group Ltd (unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2018. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Stockinger ZT, Townsend MC, McSwain NE, et al. Acute endovascular management of a subclavian artery injury. J La State Med Soc 2004;156:262–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical