Striatal Rgs4 regulates feeding and susceptibility to diet-induced obesity
- PMID: 29955167
- PMCID: PMC6310669
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-018-0120-7
Striatal Rgs4 regulates feeding and susceptibility to diet-induced obesity
Abstract
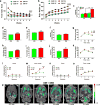
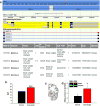
Consumption of high fat, high sugar (western) diets is a major contributor to the current high levels of obesity. Here, we used a multidisciplinary approach to gain insight into the molecular mechanisms underlying susceptibility to diet-induced obesity (DIO). Using positron emission tomography (PET), we identified the dorsal striatum as the brain area most altered in DIO-susceptible rats and molecular studies within this region highlighted regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (Rgs4) within laser-capture micro-dissected striatonigral (SN) and striatopallidal (SP) medium spiny neurons (MSNs) as playing a key role. Rgs4 is a GTPase accelerating enzyme implicated in plasticity mechanisms of SP MSNs, which are known to regulate feeding and disturbances of which are associated with obesity. Compared to DIO-resistant rats, DIO-susceptible rats exhibited increased striatal Rgs4 with mRNA expression levels enriched in SP MSNs. siRNA-mediated knockdown of striatal Rgs4 in DIO-susceptible rats decreased food intake to levels comparable to DIO-resistant animals. Finally, we demonstrated that the human Rgs4 gene locus is associated with increased body weight and obesity susceptibility phenotypes, and that overweight humans exhibit increased striatal Rgs4 protein. Our findings highlight a novel role for involvement of Rgs4 in SP MSNs in feeding and DIO-susceptibility.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hedley AA, Ogden CL, Johnson CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, Flegal KM. Prevalence of overweight and obesity among US children, adolescents, and adults, 1999-2002. JAMA. 2004;291(23):2847–2850. - PubMed
-
- Dietz WH. The response of the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to the obesity epidemic. Annu Rev Public Health. 2015;36:575–596. - PubMed
-
- Schemmel R, Mickelsen O, Tolgay Z. Dietary obesity in rats: influence of diet, weight, age, and sex on body composition. The American journal of physiology. 1969;216(2):373–379. - PubMed
-
- Fisler JS, Shimizu H, Bray GA. Brain 3-hydroxybutyrate, glutamate, and GABA in a rat model of dietary obesity. Physiol Behav. 1989;45(3):571–577. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R56 DA015446/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM062754/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DA007135/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA015446/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA006278/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA007611/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007280/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS093537/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- Z99 DA999999/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS098264/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F30 DA038954/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS086444/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA DA000069/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA023214/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AA007574/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA030359/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

