Impact factors of orthopaedic journals between 2010 and 2016: trends and comparisons with other surgical specialties
- PMID: 29955574
- PMCID: PMC6015939
- DOI: 10.21037/atm.2018.03.02
Impact factors of orthopaedic journals between 2010 and 2016: trends and comparisons with other surgical specialties
Abstract
Background: With increased legislative efforts to utilize evidence-based medicine as a guide for clinical practice, orthopaedists feel increasing pressure to publish research in higher-quality journals that reach a larger audience. Impact factor (IF) is used to quantify and rank journal apparent quality, and is the most standardized method for journal appraisal. In this study, we assessed the trends for IF among orthopaedic journals and compared these trends to those of medicine and general surgery journals.
Methods: Journal IFs from Journal Citation Reports (JCR) between the years 2010 to 2016 were obtained and analyzed for trends. Only journals that were considered primarily orthopaedic journals were included. The top 10 journals by IF in both internal medicine and surgery were also included for comparison. Each journal was analyzed by IF, and trends across time were noted. The differences in mean IF between orthopaedic specialty groups were analyzed using an independent samples t-test.
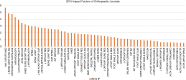
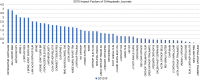
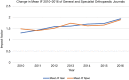
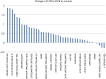
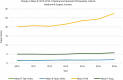
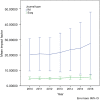
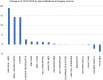
Results: The mean IF of orthopaedic increased from 1.4 (range, 0.0-3.9) in 2010 to 1.9 (range, 0.5-5.7) in 2016. In 2016, the percentage of English journals increased to 87.3% (n=48), while the percentage of journals published in the United States was 47.3% (n=26). There was a significant difference between the IF of journals published in English and those published in other languages (P=0.004). The mean IF of both general and specialized orthopaedic journals increased from 2010 to 2016, but the difference was nonsignificant. The mean IF of the top 10 journals in both surgery and internal medicine also increased from 2010 to 2016, but the increase was also nonsignificant.
Conclusions: Overall, the mean IF for peer-reviewed orthopaedic journals has increased in the past years, as has the number of journals. English journals from the United States continue to have the largest impact when compared to non-English journals and journals from outside the United States. Future studies should aim to better qualify journal impact, while limiting confounders such as self-citation.
Keywords: Orthopaedics; impact factor (IF); research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
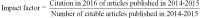
Similar articles
-
Journal Metrics of Orthopaedic Journals between 2016 and 2021: Trends and Comparisons with Other Specialties.J Knee Surg. 2024 Jul;37(9):656-663. doi: 10.1055/s-0044-1779518. Epub 2024 Jan 31. J Knee Surg. 2024. PMID: 38295832
-
Impact factors of orthopaedic journals between 2000 and 2010: trends and comparisons with other surgical specialties.Int Orthop. 2013 Apr;37(4):561-7. doi: 10.1007/s00264-012-1769-1. Epub 2013 Jan 19. Int Orthop. 2013. PMID: 23329405 Free PMC article.
-
Emergency medicine journal impact factor and change compared to other medical and surgical specialties.Acad Emerg Med. 2012 Nov;19(11):1248-54. doi: 10.1111/acem.12017. Acad Emerg Med. 2012. PMID: 23167855
-
The evolution of academic performance in emergency medicine journals: viewpoint from 2000 to 2009 journal citation reports.Acad Emerg Med. 2011 Aug;18(8):898-904. doi: 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2011.01137.x. Acad Emerg Med. 2011. PMID: 21843226 Review.
-
Open access publishing: a study of current practices in orthopaedic research.Int Orthop. 2014 Jun;38(6):1297-302. doi: 10.1007/s00264-013-2250-5. Epub 2014 Jan 3. Int Orthop. 2014. PMID: 24384939 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The most influential papers in direct anterior approach to total hip arthroplasty.Arthroplast Today. 2020 Feb 22;6(2):190-195. doi: 10.1016/j.artd.2020.01.006. eCollection 2020 Jun. Arthroplast Today. 2020. PMID: 32577460 Free PMC article.
-
Publication integrity in orthopaedic journals: the self-citation in orthopaedic research (SCOR) threshold.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2020 May;30(4):629-635. doi: 10.1007/s00590-019-02616-y. Epub 2019 Dec 20. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2020. PMID: 31858259
-
Artificial intelligence-driven analysis identifies arthroscopic shoulder surgery, meniscus injury and treatment, and total knee arthroplasty design biomechanics as the most commonly published topics in Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy.J Exp Orthop. 2025 Jul 13;12(3):e70341. doi: 10.1002/jeo2.70341. eCollection 2025 Jul. J Exp Orthop. 2025. PMID: 40655248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characteristics and Trends of the Most Cited Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research Articles.Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2022 Sep 23;14(3):38435. doi: 10.52965/001c.38435. eCollection 2022. Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2022. PMID: 36168398 Free PMC article.
-
The Altmetric Attention Score Is Associated With Citation Rates and May Reflect Academic Impact in the Total Joint Arthroplasty Literature.HSS J. 2023 Feb;19(1):37-43. doi: 10.1177/15563316221115723. Epub 2022 Aug 9. HSS J. 2023. PMID: 36776509 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bourdeau M, Winter R, Marshall R. Opportunities for improving legislative public health policy in Rhode Island through evidence-based education. R I Med J (2013) 2013;96:29-31. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
