Time-varying covariates and coefficients in Cox regression models
- PMID: 29955581
- PMCID: PMC6015946
- DOI: 10.21037/atm.2018.02.12
Time-varying covariates and coefficients in Cox regression models
Abstract
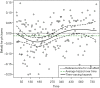
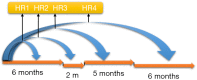
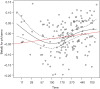
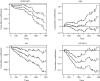
Time-varying covariance occurs when a covariate changes over time during the follow-up period. Such variable can be analyzed with the Cox regression model to estimate its effect on survival time. For this it is essential to organize the data in a counting process style. In situations when the proportional hazards assumption of the Cox regression model does not hold, we say that the effect of the covariate is time-varying. The proportional hazards assumption can be tested by examining the residuals of the model. The rejection of the null hypothesis induces the use of time varying coefficient to describe the data. The time varying coefficient can be described with a step function or a parametric time function. This article aims to illustrate how to carry out statistical analyses in the presence of time-varying covariates or coefficients with R.
Keywords: Cox proportional hazards; Schoenfeld residuals; time dependent; time varying; time-to-event.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Collett D. Modelling Survival Data in Medical Research. 3rd ed. Boca Raton: Chapman and Hall/CRC, 2014.
-
- Adeleke KA, Abiodun AA, Ipinyomi RA. Semi-parametric non-proportional hazard model with time varying covariate. Womens Health Journal 2015;14:68-87.
-
- Kalbfleisch JD, Prentice RL. The Statistical Analysis of Failure Time Data. Hoboken, NJ, USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2002.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
