Adaptation and Validation of the Malay Version of the Osteoarthritis Knee and Hip Quality of Life Questionnaire among Knee Osteoarthritis Patients
- PMID: 29955601
- PMCID: PMC6000845
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/4329751
Adaptation and Validation of the Malay Version of the Osteoarthritis Knee and Hip Quality of Life Questionnaire among Knee Osteoarthritis Patients
Abstract
Objective: To adapt and validate the Malay version of Osteoarthritis Knee and Hip Quality of Life (OAKHQOL) questionnaire.
Design: The OAKHQOL was adapted into Malay version using forward-backward translation methodology. It was then validated in a cross-sectional study of 191 patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA). Patients completed the OAKHQOL and Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) questionnaire. Confirmatory analysis, reliability analysis, and Pearson correlation test were performed.
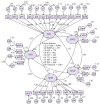
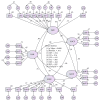
Results: The new five-factor model of 28 items demonstrated an acceptable level of goodness of fit (comparative fit index = 0.915, Tucker-Lewis index = 0.905, incremental fit index = 0.916, chi-squared/degree of freedom = 1.953, and root mean square error of approximation = 0.071), signifying a fit model. The Cronbach's alpha value and the composite reliability of each construct ranged from 0.865 to 0.933 and 0.819 to 0.921, respectively. The Pearson correlation coefficient between the OAKHQOL and the WOMAC showed adequate criterion validity. Known groups validity showed statistical difference in body mass index in physical activity, mental health, and pain construct. The pain domain was statistically different between the age groups.
Conclusion: The Malay version OAKHQOL questionnaire is a valid and reliable instrument to assess health-related quality of life in knee OA patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Arabic version of the knee and hip health-related quality of life (Mini-OAKHQOL) questionnaire in male Saudi patients with osteoarthritis: a methodological observational design.PeerJ. 2024 Sep 25;12:e18122. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18122. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39346052 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptation and validation of the Osteoarthritis Knee and Hip Quality of Life (OAKHQOL) questionnaire for use in patients with osteoarthritis in Spain.Clin Rheumatol. 2011 Dec;30(12):1563-75. doi: 10.1007/s10067-011-1855-6. Epub 2011 Sep 24. Clin Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 21947701
-
Development of a valid simplified Chinese version of the Osteoarthritis of Knee and Hip Quality of Life (OAKHQOL) in patients with knee or hip osteoarthritis.J Eval Clin Pract. 2016 Feb;22(1):53-61. doi: 10.1111/jep.12431. Epub 2015 Aug 4. J Eval Clin Pract. 2016. PMID: 26239829
-
Psychometric Properties of the Malay Language Version of Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS) Questionnaire among Knee Osteoarthritis Patients: A Confirmatory Factor Analysis.Malays Orthop J. 2017 Jul;11(2):7-14. doi: 10.5704/MOJ.1707.003. Malays Orthop J. 2017. PMID: 29021872 Free PMC article.
-
Psychometric examination of the Persian version of Osteoarthritis Knee and Hip Quality of Life questionnaire.Int J Rheum Dis. 2017 Nov;20(11):1648-1657. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.12406. Epub 2014 May 12. Int J Rheum Dis. 2017. PMID: 24818562
Cited by
-
Nutritional Status and Health-Related Quality of Life among Knee and Hip Osteoarthritis Patients under Rehabilitation Care in Kuala Nerus, Terengganu, Malaysia.Malays Orthop J. 2021 Jul;15(2):77-88. doi: 10.5704/MOJ.2107.012. Malays Orthop J. 2021. PMID: 34429826 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Arabic version of the knee and hip health-related quality of life (Mini-OAKHQOL) questionnaire in male Saudi patients with osteoarthritis: a methodological observational design.PeerJ. 2024 Sep 25;12:e18122. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18122. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39346052 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in 1‑year outcome after primary total hip and knee arthroplasty : A cohort study in older patients with osteoarthritis.Orthopade. 2019 Feb;48(2):136-143. doi: 10.1007/s00132-018-3636-2. Orthopade. 2019. PMID: 30264214 English.
-
Identifying the Psychometric Properties of the Malay Version of the WHOQOL-BREF among Employees with Obesity Problem.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jun 20;19(12):7542. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19127542. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35742790 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the open kinetic chain and closed kinetic chain strengthening exercises on pain perception and lower limb biomechanics of patients with mild knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial protocol.Trials. 2022 Apr 15;23(1):315. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06153-8. Trials. 2022. PMID: 35428274 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Tejada M. G. S., et al. Adaptation and validation of the Osteoarthritis Knee and Hip Quality of Life (OAKHQOL) questionnaire for use in patients with osteoarthritis in Spain. Clinical Rheumatology. 2011;30(12):1563–1575. - PubMed
-
- Lapsley H. M., et al. Living with osteoarthritis: patient expenditures, health status, and social impact. Arthritis Care & Research. 2001;45(3):301–306. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

