Utilisation of an operative difficulty grading scale for laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- PMID: 29956029
- PMCID: PMC6336748
- DOI: 10.1007/s00464-018-6281-2
Utilisation of an operative difficulty grading scale for laparoscopic cholecystectomy
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Utilisation of an operative difficulty grading scale for laparoscopic cholecystectomy.Surg Endosc. 2019 Jan;33(1):122-125. doi: 10.1007/s00464-018-6377-8. Surg Endosc. 2019. PMID: 30136037 Free PMC article.
-
Correction to: Surgical Endoscopy-Author name correction.Surg Endosc. 2023 Mar;37(3):2415. doi: 10.1007/s00464-023-09888-w. Surg Endosc. 2023. PMID: 36764937 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: A reliable system for grading operative difficulty of laparoscopic cholecystectomy would standardise description of findings and reporting of outcomes. The aim of this study was to validate a difficulty grading system (Nassar scale), testing its applicability and consistency in two large prospective datasets.
Methods: Patient and disease-related variables and 30-day outcomes were identified in two prospective cholecystectomy databases: the multi-centre prospective cohort of 8820 patients from the recent CholeS Study and the single-surgeon series containing 4089 patients. Operative data and patient outcomes were correlated with Nassar operative difficultly scale, using Kendall's tau for dichotomous variables, or Jonckheere-Terpstra tests for continuous variables. A ROC curve analysis was performed, to quantify the predictive accuracy of the scale for each outcome, with continuous outcomes dichotomised, prior to analysis.
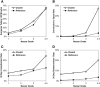
Results: A higher operative difficulty grade was consistently associated with worse outcomes for the patients in both the reference and CholeS cohorts. The median length of stay increased from 0 to 4 days, and the 30-day complication rate from 7.6 to 24.4% as the difficulty grade increased from 1 to 4/5 (both p < 0.001). In the CholeS cohort, a higher difficulty grade was found to be most strongly associated with conversion to open and 30-day mortality (AUROC = 0.903, 0.822, respectively). On multivariable analysis, the Nassar operative difficultly scale was found to be a significant independent predictor of operative duration, conversion to open surgery, 30-day complications and 30-day reintervention (all p < 0.001).
Conclusion: We have shown that an operative difficulty scale can standardise the description of operative findings by multiple grades of surgeons to facilitate audit, training assessment and research. It provides a tool for reporting operative findings, disease severity and technical difficulty and can be utilised in future research to reliably compare outcomes according to case mix and intra-operative difficulty.
Keywords: Cholecystectomy; Difficulty grading; Laparoscopic; Operative difficulty; Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
Drs. Griffiths, Hodson, Vohra, Marriott, Katbeh, Zino and Nassar have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Nassar AHM, Ashkar KA, Mohamed AY, Hafiz AA (1995) Is laparoscopic cholecystectomy possible without video technology? Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 4:63–65 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources