Size-Dependent Segregation Controls Macrophage Phagocytosis of Antibody-Opsonized Targets
- PMID: 29958103
- PMCID: PMC6067926
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.05.059
Size-Dependent Segregation Controls Macrophage Phagocytosis of Antibody-Opsonized Targets
Abstract
Macrophages protect the body from damage and disease by targeting antibody-opsonized cells for phagocytosis. Though antibodies can be raised against antigens with diverse structures, shapes, and sizes, it is unclear why some are more effective at triggering immune responses than others. Here, we define an antigen height threshold that regulates phagocytosis of both engineered and cancer-specific antigens by macrophages. Using a reconstituted model of antibody-opsonized target cells, we find that phagocytosis is dramatically impaired for antigens that position antibodies >10 nm from the target surface. Decreasing antigen height drives segregation of antibody-bound Fc receptors from the inhibitory phosphatase CD45 in an integrin-independent manner, triggering Fc receptor phosphorylation and promoting phagocytosis. Our work shows that close contact between macrophage and target is a requirement for efficient phagocytosis, suggesting that therapeutic antibodies should target short antigens in order to trigger Fc receptor activation through size-dependent physical segregation.
Keywords: CD45; Fc receptor; ITAM; antibody; antigen; cancer immunotherapy; immune modulation; kinetic segregation model; macrophages; phagocytosis; protein segregation.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
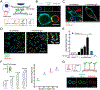

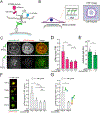



References
-
- Williams AF, and Barclay AN (1988). The Immunoglobulin Superfamily—Domains for Cell Surface Recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol 6, 381–405. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, and Takeda K (2004). Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol 4, 499–511. - PubMed
-
- Anton van der Merwe P, Davis SJ, Shaw AS, and Dustin ML (2000). Cytoskeletal polarization and redistribution of cell-surface molecules during T cell antigen recognition. Semin. Immunol 12, 5–21. - PubMed
-
- Baselga J (2001). Clinical trials of Herceptin® (trastuzumab). Eur. J. Cancer 37, 1824. - PubMed
-
- Beauchemin N, and Arabzadeh A (2013). Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecules (CEACAMs) in cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 32, 643–671. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

