Increased CYFRA 21-1, CEA and NSE are Prognostic of Poor Outcome for Locally Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Lung: A Nomogram and Recursive Partitioning Risk Stratification Analysis
- PMID: 29958123
- PMCID: PMC6040260
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2018.05.008
Increased CYFRA 21-1, CEA and NSE are Prognostic of Poor Outcome for Locally Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Lung: A Nomogram and Recursive Partitioning Risk Stratification Analysis
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to: (1) assess the prognostic significance of serum tumor markers in locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma in lung (LA-SCCL); (2) generate a nomogram to predict the overall survival (OS) and (3) identify a prognostic stratification to assist the therapeutic decision-making.
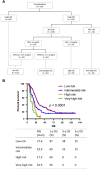
Methods: LA-SCCL patients receiving definitive radiotherapy and baseline tumor marker measurement were eligible for this retrospective study. Cox proportional hazards regression was used to determine independent factors associated with various survival indexes and a nomogram was created to estimate the 5-year OS probability for individual patient. The identified prognostic factors were recruited into a recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) for OS to stratify patients with distinct outcome.
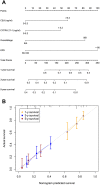
Results: A total of 224 patients were eligible for analysis. Increased cytokeratin-19 fragment (CYFRA 21-1) was independently associated with inferior OS, progression free survival (PFS) and a borderline decreased local-regional progression free survival (LRPFS). Elevated carcino-embryonic antigen (CEA) served as an unfavorable determinant for OS and increased neuron-specific enolase (NSE) was predictive of poor distant metastasis free survival (DMFS). A nomogram integrating KPS, TNM stage, CEA and CYFRA 21-1 was created, resulting in a c-index of 0.62. RPA identified 4 prognostic classifications, with median OS of 27.6, 19.9, 17.3 and 10.9 months for low, intermediate, high and very-high risk groups, respectively.
Conclusions: Baseline tumor marker panel including CYFRA 21-1, CEA and NSE can be prognostic of outcome for LA-SCCL receiving definitive radiotherapy. The RPA identified four prognostic subgroups, which could assist personalized therapy and clinical trial design in LA-SCCL.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Wang J, Zhou Z, Liang J, Feng Q, Xiao Z, Hui Z, Wang X, Lv J, Chen D, Zhang H. Intensity-modulated radiation therapy may improve local-regional tumor control for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer compared with three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy. Oncologist. 2016;21:1530–1537. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kong J, F Xu, He M, Chen K, Qian B. The incidence of lung cancer by histological type: A population-based study in tianjin, china during 1981-2005. Respirology. 2014;19:1222–1228. - PubMed
-
- Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH, Chu DT, Saijo N, Sunpaweravong P, Han B, Margono B, Ichinose Y. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:947–957. - PubMed
-
- Solomon BJ, Mok T, Kim DW, YL Wu, Nakagawa K, Mekhail T, Felip E, Cappuzzo F, Paolini J, Usari T. First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2167–2177. - PubMed
-
- Kulpa J, Wojcik E, Reinfuss M, Kolodziejski L. Carcinoembryonic antigen, squamous cell carcinoma antigen, CYFRA 21-1, and neuron-specific enolase in squamous cell lung cancer patients. Clin Chem. 2002;48:1931–1937. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

