Using Interpretative Structural Modeling to Identify Critical Success Factors for Safety Management in Subway Construction: A China Study
- PMID: 29958438
- PMCID: PMC6069219
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph15071359
Using Interpretative Structural Modeling to Identify Critical Success Factors for Safety Management in Subway Construction: A China Study
Abstract
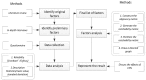
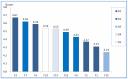
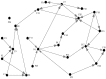
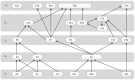
With the rapid development of urbanization in China, a vast number of subway projects are under construction and planned in many cities. However, the complexities of the environment in subway construction inherently bring about many uncertainties and risk factors. Understanding the inherent properties of the critical success factors (CSFs) will contribute significantly to the subway construction. From this perspective, this paper aims to identify the CSFs for safety management in subway construction. This study screened preliminary CSFs through a literature review and in-depth interviews with experts in China. Based on the data gathered and subsequently analyzed from the questionnaire surveys, a final total of 24 CSFs were identified. Then, interpretative structural modeling was employed to ascertain the interrelations among them. The result showed that the factors concerning the engineering survey and design not only occupy relatively higher scores in the questionnaire survey but also contribute significantly latent impacts on other factors. In addition, the creation of a reasonable schedule and the investment of the safety measures were also found to have a fundamental impact on the safety management of subway construction. This research guided the safety managers in determining the most important safety factors they must face and provided them valuable information that could promote safety performance and decrease the number of accidents over the course of subway construction.
Keywords: critical success factors; interpretative structural modeling; safety; subway construction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ding L., Zhang L., Wu X., Skibniewski M.J., Yu Q. Safety management in tunnel construction: Case study of Wuhan metro construction in China. Saf. Sci. 2014;62:8–15. doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2013.07.021. - DOI
-
- Choi H.H., Cho H.N., Seo J.W. Risk Assessment Methodology for Underground Construction Projects. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2004;130:258–272. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9364(2004)130:2(258). - DOI
-
- Zhou Z., Irizarry J. Integrated Framework of Modified Accident Energy Release Model and Network Theory to Explore the Full Complexity of the Hangzhou Subway Construction Collapse. J. Manag. Eng. 2016;32:5016013. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)ME.1943-5479.0000431. - DOI
-
- Hollnagel E. Safety-I and Safety-II: The Past and Future of Safety Management. Ashgate Publishing Company; Farnham, UK: 2014.
-
- Hollnagel E. Prologue: The Scope of Resilience Engineering. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd.; Surrey, UK: 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources