Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus: A Structural View
- PMID: 29958443
- PMCID: PMC6071267
- DOI: 10.3390/v10070350
Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus: A Structural View
Abstract
Tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) is a growing health concern. It causes a severe disease that can lead to permanent neurological complications or death and the incidence of TBEV infections is constantly rising. Our understanding of TBEV’s structure lags behind that of other flaviviruses, but has advanced recently with the publication of a high-resolution structure of the TBEV virion. The gaps in our knowledge include: aspects of receptor binding, replication and virus assembly. Furthermore, TBEV has mostly been studied in mammalian systems, even though the virus’ interaction with its tick hosts is a central part of its life cycle. Elucidating these aspects of TBEV biology are crucial for the development of TBEV antivirals, as well as the improvement of diagnostics. In this review, we summarise the current structural knowledge on TBEV, bringing attention to the current gaps in our understanding, and propose further research that is needed to truly understand the structural-functional relationship of the virus and its hosts.
Keywords: E protein; M protein; TBEV; envelope protein; flavivirus structure; maturation; nucleocapsid; prM; tick-borne encephalitis virus; virus assembly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the writing of the manuscript or in the decision to publish.
Figures
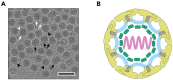

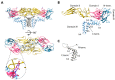

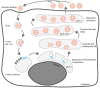
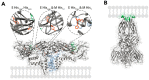
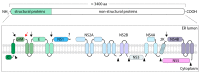
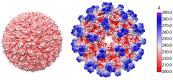
References
-
- Grard G., Moureau G., Charrel R.N., Lemasson J.J., Gonzalez J.P., Gallian P., Gritsun T.S., Holmes E.C., Gould E.A., de Lamballerie X. Genetic characterization of tick-borne flaviviruses: New insights into evolution, pathogenetic determinants and taxonomy. Virology. 2007;361:80–92. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.09.015. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

