Longevity of duodenal and peripheral T-cell and humoral responses to live-attenuated Salmonella Typhi strain Ty21a
- PMID: 29958737
- PMCID: PMC6041722
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2018.05.114
Longevity of duodenal and peripheral T-cell and humoral responses to live-attenuated Salmonella Typhi strain Ty21a
Abstract
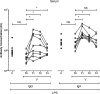
Background: We have previously demonstrated that polyfunctional Ty21a-responsive CD4+ and CD8+ T cells are generated at the duodenal mucosa 18 days following vaccination with live-attenuated S. Typhi (Ty21a). The longevity of cellular responses has been assessed in peripheral blood, but persistence of duodenal responses is unknown.
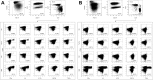
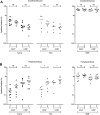
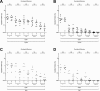
Methods: We vaccinated eight healthy adults with Ty21a. Peripheral blood and duodenal samples were acquired after a median of 1.5 years (ranging from 1.1 to 3.7 years) following vaccination. Cellular responses were assessed in peripheral blood and at the duodenal mucosa by flow cytometry. Levels of IgG and IgA were also assessed in peripheral blood by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Results: No T-cell responses were observed at the duodenal mucosa, but CD4+ T-cell responses to Ty21a and FliC were observed in peripheral blood. Peripheral anti-lipopolysaccharide IgG and IgA responses were also observed. Early immunoglobulin responses were not associated with the persistence of long-term cellular immune responses.
Conclusions: Early T-cell responses which we have previously observed at the duodenal mucosa 18 days following oral vaccination with Ty21a could not be detected at a median of 1.5 years. Peripheral responses were observed at this time. Immunoglobulin responses observed shortly after vaccination were not associated with cellular immune responses at 1.5 years, suggesting that the persistence of cellular immunity is not associated with the strength of the initial humoral response to vaccination.
Keywords: Cytokines; Immunoglobulins; Salmonella; T cells; Ty21a.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Parry C.M., Hien T.T., Dougan G., White N.J., Farrar J.J. Typhoid fever. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1770–1782. - PubMed
-
- Germanier R., Fuer E. Isolation and characterization of Gal E mutant Ty 21a of Salmonella typhi: a candidate strain for a live, oral typhoid vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1975;131:553–558. - PubMed
-
- Anwar E, Goldberg E, Fraser A, Acosta CJ, Paul M, Leibovici L. Vaccines for preventing typhoid fever. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014;1:CD001261.
-
- Olanratmanee T., Levine M., Losonsky G., Thisyakorn V., Cryz S.J., Jr. Safety and immunogenicity of Salmonella typhi Ty21a liquid formulation vaccine in 4- to 6-year-old Thai children. J Infect Dis. 1992;166:451–452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

