Tumor Cell-Intrinsic Factors Underlie Heterogeneity of Immune Cell Infiltration and Response to Immunotherapy
- PMID: 29958801
- PMCID: PMC6707727
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.06.006
Tumor Cell-Intrinsic Factors Underlie Heterogeneity of Immune Cell Infiltration and Response to Immunotherapy
Abstract
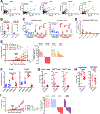
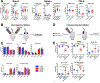
The biological and functional heterogeneity between tumors-both across and within cancer types-poses a challenge for immunotherapy. To understand the factors underlying tumor immune heterogeneity and immunotherapy sensitivity, we established a library of congenic tumor cell clones from an autochthonous mouse model of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. These clones generated tumors that recapitulated T cell-inflamed and non-T-cell-inflamed tumor microenvironments upon implantation in immunocompetent mice, with distinct patterns of infiltration by immune cell subsets. Co-injecting tumor cell clones revealed the non-T-cell-inflamed phenotype is dominant and that both quantitative and qualitative features of intratumoral CD8+ T cells determine response to therapy. Transcriptomic and epigenetic analyses revealed tumor-cell-intrinsic production of the chemokine CXCL1 as a determinant of the non-T-cell-inflamed microenvironment, and ablation of CXCL1 promoted T cell infiltration and sensitivity to a combination immunotherapy regimen. Thus, tumor cell-intrinsic factors shape the tumor immune microenvironment and influence the outcome of immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
The authors have no competing interests.
Figures





Comment in
-
Tumour decides immune cell ins and outs.Nat Rev Immunol. 2018 Aug;18(8):481. doi: 10.1038/s41577-018-0038-y. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29985485 No abstract available.
-
A Tumor Cell-Intrinsic Yin-Yang Determining Immune Evasion.Immunity. 2018 Jul 17;49(1):11-13. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.07.001. Immunity. 2018. PMID: 30021140 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

