Conformation-dependent binding of a Tetrastatin peptide to αvβ3 integrin decreases melanoma progression through FAK/PI3K/Akt pathway inhibition
- PMID: 29959360
- PMCID: PMC6026150
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-28003-x
Conformation-dependent binding of a Tetrastatin peptide to αvβ3 integrin decreases melanoma progression through FAK/PI3K/Akt pathway inhibition
Abstract
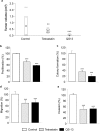
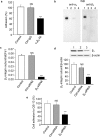
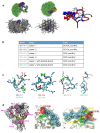
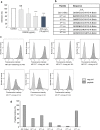
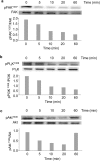
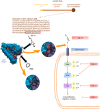
Tetrastatin, a 230 amino acid sequence from collagen IV, was previously demonstrated to inhibit melanoma progression. In the present paper, we identified the minimal active sequence (QKISRCQVCVKYS: QS-13) that reproduced the anti-tumor effects of whole Tetrastatin in vivo and in vitro on melanoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion. We demonstrated that QS-13 binds to SK-MEL-28 melanoma cells through the αvβ3 integrin using blocking antibody and β3 integrin subunit siRNAs strategies. Relevant QS-13 conformations were extracted from molecular dynamics simulations and their interactions with αVβ3 integrin were analyzed by docking experiments to determine the binding areas and the QS-13 amino acids crucial for the binding. The in silico results were confirmed by in vitro experiments. Indeed, QS-13 binding to SK-MEL-28 was dependent on the presence of a disulfide-bound as shown by mass spectroscopy and the binding site on αVβ3 was located in close vicinity to the RGD binding site. QS-13 binding inhibits the FAK/PI3K/Akt pathway, a transduction pathway that is largely involved in tumor cell proliferation and migration. Taken together, our results demonstrate that the QS-13 peptide binds αvβ3 integrin in a conformation-dependent manner and is a potent antitumor agent that could target cancer cells through αVβ3.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The anti-tumor NC1 domain of collagen XIX inhibits the FAK/ PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway through αvβ3 integrin interaction.Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 12;7(2):1516-28. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6399. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26621838 Free PMC article.
-
Disintegrin Tablysin-15 Suppresses Cancer Hallmarks in Melanoma Cells by Blocking FAK/Akt/ERK and NF-κB Signaling.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2020;20(4):306-315. doi: 10.2174/1568009620666200101094736. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2020. PMID: 31893992
-
CCN3 increases cell motility and MMP-13 expression in human chondrosarcoma through integrin-dependent pathway.J Cell Physiol. 2011 Dec;226(12):3181-9. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22672. J Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21344378
-
Type XIX collagen: A new partner in the interactions between tumor cells and their microenvironment.Matrix Biol. 2017 Jan;57-58:169-177. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2016.07.010. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Matrix Biol. 2017. PMID: 27491275 Review.
-
Nano-Strategies Targeting the Integrin αvβ3 Network for Cancer Therapy.Cells. 2021 Jul 3;10(7):1684. doi: 10.3390/cells10071684. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34359854 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular matrix-derived peptides in tissue remodeling and fibrosis.Matrix Biol. 2020 Sep;91-92:176-187. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2020.04.006. Epub 2020 May 8. Matrix Biol. 2020. PMID: 32438055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Silico Prediction of Tetrastatin-Derived Peptide Interactions with αvβ3 and α5β1 Integrins.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jun 21;18(7):940. doi: 10.3390/ph18070940. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40732230 Free PMC article.
-
Truncated O-Glycan-Bearing MUC16 Enhances Pancreatic Cancer Cells Aggressiveness via α4β1 Integrin Complexes and FAK Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 13;23(10):5459. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105459. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628269 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Adhesion Molecules in Plasticity and Metastasis.Mol Cancer Res. 2021 Jan;19(1):25-37. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-20-0595. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Mol Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33004622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor Microenvironment: Extracellular Matrix Alterations Influence Tumor Progression.Front Oncol. 2020 Apr 15;10:397. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00397. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32351878 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhou J, Ding M, Zhao Z, Reeders ST. Complete primary structure of the sixth chain of human basement membrane collagen, alpha 6(IV). Isolation of the cDNAs for alpha 6(IV) and comparison with five other type IV collagen chains. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:13193–13199. - PubMed
-
- Colorado PC, et al. Anti-angiogenic Cues from Vascular Basement Membrane Collagen. Cancer Res. 2000;60:2520–2526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

