FOXM1 predicts disease progression in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer
- PMID: 29959570
- PMCID: PMC6096766
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-018-2694-5
FOXM1 predicts disease progression in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer
Abstract
Purpose: The proto-oncogene forkhead box M1 (FOXM1) is associated with poor survival in many cancers. The impact of FOXM1 expression on progression-free survival (PFS) of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) has not yet been investigated. The differential expression of FOXM1 between the different molecular NMIBC subtypes has further been assessed.
Methods: Transcript levels of FOXM1 and MKI67 were determined in 460 NMIBC patients (UROMOL cohort) by RNA-Seq and validated in silico by the Chungbuk and Lund cohort (n = 277). FOXM1 and MKI67 cutoffs were identified by the minimal p value method. Variables were evaluated by multivariable Cox regression analyses in order to identify independent predictors.
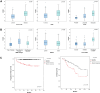
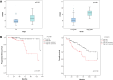
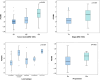
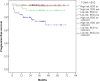
Results: FOXM1 is an independent predictor for PFS superior to current histological, clinical and molecular staging methods. Patients with high FOXM1 expression have a 6- to 8-fold higher risk of progression in multivariable analysis (p < 0.03). Highest transcript levels were found in the Class 2 and genomically unstable molecular NMIBC subtype (p < 0.03). The proto-oncogene further positively correlated with tumor grade and stage. NMIBCs with high FOXM1 expression showed a PFS advantage when treated with intravesical BCG instillation.
Conclusion: FOXM1 is a highly prognostic marker for disease progression of NMIBC superior to current histological, clinical and molecular staging methods and MKI67. It is mainly expressed in the Class 2 and genomically unstable molecular bladder cancer subtypes. Its role in drug resistance development makes FOXM1 valuable biomarker for NMIBC risk stratification.
Keywords: Biomarker; Bladder cancer; FOXM1; MKI67; Molecular subtypes; Progression-free survival.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare to have no COIs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
FOXM1 overexpression is associated with adverse outcome and predicts response to intravesical instillation therapy in stage pT1 non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.BJU Int. 2019 Jan;123(1):187-196. doi: 10.1111/bju.14525. Epub 2018 Sep 9. BJU Int. 2019. PMID: 30120861
-
Expression signature defined by FOXM1-CCNB1 activation predicts disease recurrence in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Jun 15;20(12):3233-43. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-2761. Epub 2014 Apr 8. Clin Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24714775
-
FOXM1 predicts overall and disease specific survival in muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma and presents a differential expression between bladder cancer subtypes.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 18;8(29):47595-47606. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17394. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28498805 Free PMC article.
-
FoxM1: Repurposing an oncogene as a biomarker.Semin Cancer Biol. 2018 Oct;52(Pt 1):74-84. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.08.009. Epub 2017 Sep 10. Semin Cancer Biol. 2018. PMID: 28855104 Review.
-
Molecular biomarkers of progression in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer - beyond conventional risk stratification.Nat Rev Urol. 2025 Feb;22(2):75-91. doi: 10.1038/s41585-024-00914-7. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Nat Rev Urol. 2025. PMID: 39095581 Review.
Cited by
-
Urinary bladder cancer needs more attention - recommendations for health care professionals and politicians in the European Union.Nat Rev Urol. 2025 Aug 19. doi: 10.1038/s41585-025-01077-9. Online ahead of print. Nat Rev Urol. 2025. PMID: 40830244 Review.
-
Integrative Transcriptome Profiling Reveals SKA3 as a Novel Prognostic Marker in Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Sep 17;13(18):4673. doi: 10.3390/cancers13184673. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34572901 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Key Genes Associated with Progression and Prognosis of Bladder Cancer through Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 25;13(23):5931. doi: 10.3390/cancers13235931. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34885040 Free PMC article.
-
FOXM1 functions collaboratively with PLAU to promote gastric cancer progression.J Cancer. 2020 Jan 1;11(4):788-794. doi: 10.7150/jca.37323. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31949481 Free PMC article.
-
Circ-MMP2 (circ-0039411) induced by FOXM1 promotes the proliferation and migration of lung adenocarcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jun 8;11(6):426. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2628-4. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32513952 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Babjuk M, Böhle A, Burger M et al (2017) EAU guidelines on non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: update 2016. Eur Urol 71:447–461. 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.05.041 - PubMed
-
- Contreras-Sanz A, Roberts ME, Seiler R, Black PC (2017) Recent progress with next-generation biomarkers in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Int J Urol Off J Jpn Urol Assoc 24:7–15. 10.1111/iju.13193 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

