Phase II study of ceritinib in alectinib-pretreated patients with anaplastic lymphoma kinase-rearranged metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer in Japan: ASCEND-9
- PMID: 29959809
- PMCID: PMC6125456
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.13721
Phase II study of ceritinib in alectinib-pretreated patients with anaplastic lymphoma kinase-rearranged metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer in Japan: ASCEND-9
Abstract
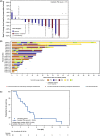
Clinical experience of ceritinib in patients who progressed on alectinib is limited. In this prospective phase II study, we evaluated the activity of ceritinib in alectinib-pretreated patients with anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-rearranged metastatic (stage IIIB/IV) non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in Japan. All patients were required to have ≥1 measurable lesion per RECIST, 1.1, and a World Health Organization Performance Status (WHO PS) of 0-1. Prior crizotinib and/or up to 1 chemotherapy regimen was allowed. Primary endpoint was investigator-assessed overall response rate (ORR) per RECIST 1.1. Ceritinib was given at a dose of 750 mg/day fasted. A total of 20 patients were enrolled from August 2015 to March 2017. All patients received prior alectinib (100%), 13 (65.0%) patients received prior platinum-based chemotherapy, and 4 (20%) patients received prior crizotinib. Median duration of exposure and the follow-up time with ceritinib were 3.7 months (range: 0.4-15.1) and 11.6 months (range: 4.8-23.0), respectively. Investigator-assessed ORR was 25% (95% CI: 8.7-49.1). Key secondary endpoints, all investigator assessed, included disease control rate (70.0%; 95% CI: 45.7-88.1), time to response (median, 1.8 months; range: 1.8-2.0), and duration of response (median, 6.3 months; 95% CI: 3.5-9.2). Median progression-free survival was 3.7 months (95% CI: 1.9-5.3). The most common adverse events reported were diarrhea (85.0%), nausea (80.0%), and vomiting (65.0%). Based on our findings, ceritinib could be considered as one of the treatment options for patients with ALK-positive NSCLC who progressed on alectinib. (Trial registration no. NCT02450903).
Keywords: ALK; Japan; NSCLC; anaplastic lymphoma kinase; ceritinib.
© 2018 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
References
-
- Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4‐ALK fusion gene in non‐small‐cell lung cancer. Nature. 2007;448:561‐566. - PubMed
-
- US Food and Drug Administration . Crizotinib US prescribing information. 2014. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/202570s011lbl.pdf. Accessed May 23, 2018.
-
- Solomon BJ, Mok T, Kim D‐W, et al. First‐line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK‐positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2167‐2177. - PubMed
-
- Shaw AT, Kim DW, Nakagawa K, et al. Crizotinib versus chemotherapy in advanced ALK‐positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:2385‐2394. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

