Conflict of interest among Italian medical oncologists: a national survey
- PMID: 29961019
- PMCID: PMC6042593
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-020912
Conflict of interest among Italian medical oncologists: a national survey
Abstract
Objectives: To assess Italian medical oncologists' opinion on the implications of conflict of interest (COI) on medical education, care and research, and to evaluate their direct financial relationships.
Design: National cross-sectional survey conducted between March and April 2017 among Italian oncologists.
Setting: Online survey sponsored by the Italian College of Medical Oncology Chiefs through its website.
Participants: Italian oncologists who filled out an anonymous questionnaire including 19 items and individual and working characteristics.
Main outcome measure: The proportion of medical oncologists perceiving COI as an outstanding issue and those receiving direct payments from industry.
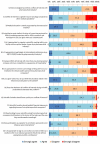
Results: There were 321 respondents, representing 13% of Italian tenured medical oncologists. Overall, 62% declared direct payments from the pharmaceutical industry in the last 3 years. Sixty-eight per cent felt the majority of Italian oncologists have a COI with industry, but 59% suppose this is not greater than that of other specialties. Eighty-two per cent consider that most oncology education is supported by industry. More than 75% believe that current allocation of industry budget on marketing and promotion rather than research and development is unfair, but 75% consider it appropriate to receive travel and lodging hospitality from industry. A median net profit margin of €5000 per patient enrolled in an industry trial was considered appropriate for the employee institution. Sixty per cent agree to receive a personal fee for patients enrolled in industry trials, but 79% state this should be reported in the informed consent. Over 90% believe that scientific societies should publish a financial report of industry support. Finally, 79% disagree to being a coauthor of an article written by a medical writer when no substantial scientific contribution is made.
Conclusions: Among Italian oncologists COI is perceived as an important issue influencing costs, education, care and science. A more rigorous policy on COI should be implemented.
Keywords: cancer drug prices; conflict of interest; ghost writing; physician industry relationship; survey oncologist.
© Article author(s) (or their employer(s) unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2018. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous