Intermittent Hypoxia Induced Formation of "Endothelial Cell-Colony Forming Units (EC-CFUs)" Is Affected by ROS and Oxidative Stress
- PMID: 29963003
- PMCID: PMC6010519
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00447
Intermittent Hypoxia Induced Formation of "Endothelial Cell-Colony Forming Units (EC-CFUs)" Is Affected by ROS and Oxidative Stress
Abstract
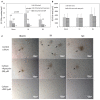
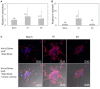
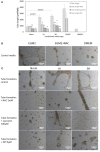
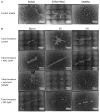
Intermittent hypoxia (IH)-the hallmark of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)-increases leukocyte activation, production of NADPH-oxidase dependent reactive oxygen species (ROS) and oxidative stress, affecting endothelial function. However, IH and oxidative stress can also stimulate adaptive-protective mechanisms by inducing the development of Endothelial Cell-Colony Forming Units (EC-CFUs), which are considered as a good surrogate marker for endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs), and likely reflect a reparatory response to vascular damage or tissue ischemia by leukocytes. Blood samples were obtained from 15 healthy consenting volunteers to evaluate the effects of IH and sustained hypoxia (SH) in vitro on EC-CFUs development and functions. The variables measured included: their numbers, the area, the proliferative capacity and ROS production. Additionally, NADPH-oxidase, VEGF and nuclear factor-erythroid 2 related factor 2 (Nrf2) expression, as well as their paracrine effects on endothelial tube formation were determined. The involvement of ROS was probed using the anti-oxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and NADPH-oxidase inhibitors apocynin and diphenyl-iodide. Compared to normoxia, IH-dependent increases in EC-CFUs numbers were observed, showing an individual donor-dependent trait. Also, the expression of VEGF and gp91phox, a subunit of NADPH-oxidase, were significantly increased. ROS production and oxidative stress markers were also significantly increased, but Nrf2 expression and colony size were unaffected by IH. Additionally, conditioned media harvested from IH- and SH-treated mature EC-CFUs, significantly increased endothelial tube formation. These effects were markedly attenuated or diminished by the ROS and NADPH-oxidase inhibitors employed. In conclusion, we show here for the first time that IH-associated oxidative stress promotes EC-CFUs' vascular and paracrine capacities through ROS. However, the large inter-individual variability expressed in EC-CFUs numbers and functions to a given IH stimulus, may represent an individual trait with a potential clinical significance.
Keywords: N-acetylcysteine; NADPH oxidase inhibitors; endothelial cell-colony forming units (EC-CFUs); endothelial tube formation; intermittent hypoxia; obstructive sleep apnea; oxidative-stress.
Figures







References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

