Comparison of Outcomes between Direct-to-Implant Breast Reconstruction Following Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy through Inframammary Fold Incision versus Noninframammary Fold Incision
- PMID: 29963118
- PMCID: PMC6015980
- DOI: 10.4048/jbc.2018.21.2.213
Comparison of Outcomes between Direct-to-Implant Breast Reconstruction Following Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy through Inframammary Fold Incision versus Noninframammary Fold Incision
Abstract
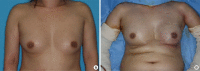
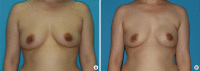
Purpose: In properly selected patients with breast cancer, nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM) is generally considered safe by oncologic standards. We examined two groups of patients who underwent direct-to-implant (DTI) reconstruction after NSM, comparing complications encountered, revision rates, and aesthetic outcomes. The patients were stratified based on type of surgical incision and assigned to inframammary fold (IMF) and non-IMF groups.
Methods: We investigated 141 patients (145 breasts) subjected to NSM and immediate DTI reconstruction between 2013 and 2016. A total of 62 breasts (in 58 patients) were surgically removed via IMF incisions, with the other 83 breasts (in 83 patients) removed by non-IMF means.
Results: Complications associated with IMF (n=62) and non-IMF (n=83) incisions were as follows: skin necrosis (IMF, 9; non-IMF, 18); hematoma (IMF, 3; non-IMF, 4); seroma (IMF, 8; non-IMF, 4); mild capsular contracture (IMF, 4; non-IMF, 7); and tumor recurrence (IMF, 2; non-IMF, 8). Surgical revisions were counted as duplicates (IMF, 18; non-IMF, 38). Aesthetic outcomes following IMF incisions were rated as very good (44.2%), good (23.1%), fair (23.1%), or poor (9.6%).
Conclusion: IMF incision enables complete preservation of the nipple-areolar complex, yielding superior aesthetic results in immediate DTI breast reconstruction after NSM. The nature of incision used had no significant impact on postoperative complications or reoperation rates and had comparable oncologic safety to that of non-IMF incisions. IMF incisions produced the least visible scarring and did not affect breast shape. Most patients were satisfied with the aesthetic outcomes.
Keywords: Breast implants; Mammaplasty; Mastectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessing aesthetic outcomes of different incision types for nipple-sparing mastectomy followed by radiation therapy in prepectoral direct-to-implant breast reconstruction: a retrospective study.World J Surg Oncol. 2025 Mar 15;23(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s12957-025-03730-4. World J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40089730 Free PMC article.
-
Inframammary Fold Incision Can Reduce Skin Flap Necrosis in Immediate Breast Reconstruction With Implant and Conjoined Fascial Flap.Ann Plast Surg. 2020 Nov;85(5):488-494. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000002393. Ann Plast Surg. 2020. PMID: 32332387
-
Comparison of complications according to incision types in nipple-sparing mastectomy and immediate reconstruction.Breast. 2020 Oct;53:85-91. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2020.06.009. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Breast. 2020. PMID: 32653836 Free PMC article.
-
Defining a place for nipple sparing mastectomy in modern breast care: an evidence based review.Breast J. 2013 Nov-Dec;19(6):571-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4741.2011.01220.x. Epub 2012 Jan 29. Breast J. 2013. PMID: 22284266 Review.
-
Nipple sparing mastectomy and the evolving direct to implant breast reconstruction.Gland Surg. 2018 Jun;7(3):267-272. doi: 10.21037/gs.2017.08.06. Gland Surg. 2018. PMID: 29998076 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Direct-to-implant breast reconstruction following nipple-sparing mastectomy: predictive factors of adverse surgical outcomes in Asian patients.Arch Plast Surg. 2021 Sep;48(5):483-493. doi: 10.5999/aps.2021.00374. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Arch Plast Surg. 2021. PMID: 34583432 Free PMC article.
-
Timing between Breast Reconstruction and Oncologic Mastectomy-One Center Experience.Medicina (Kaunas). 2020 Feb 20;56(2):86. doi: 10.3390/medicina56020086. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020. PMID: 32093278 Free PMC article.
-
Oncoplastic and Reconstructive Breast Surgery: A Comprehensive Review.Cureus. 2022 Jan 31;14(1):e21763. doi: 10.7759/cureus.21763. eCollection 2022 Jan. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35251834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing aesthetic outcomes of different incision types for nipple-sparing mastectomy followed by radiation therapy in prepectoral direct-to-implant breast reconstruction: a retrospective study.World J Surg Oncol. 2025 Mar 15;23(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s12957-025-03730-4. World J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40089730 Free PMC article.
-
Scar Healing after Breast Reconstruction: A 5-year Follow-up in Asian Patients.J Plast Reconstr Surg. 2024 Aug 23;4(1):20-25. doi: 10.53045/jprs.2024-0013. eCollection 2025 Jan 27. J Plast Reconstr Surg. 2024. PMID: 40160955 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Didier F, Radice D, Gandini S, Bedolis R, Rotmensz N, Maldifassi A, et al. Does nipple preservation in mastectomy improve satisfaction with cosmetic results, psychological adjustment, body image and sexuality? Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009;118:623–633. - PubMed
-
- Didier F, Arnaboldi P, Gandini S, Maldifassi A, Goldhirsch A, Radice D, et al. Why do women accept to undergo a nipple sparing mastectomy or to reconstruct the nipple areola complex when nipple sparing mastectomy is not possible? Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;132:1177–1184. - PubMed
-
- Jensen JA, Orringer JS, Giuliano AE. Nipple-sparing mastectomy in 99 patients with a mean follow-up of 5 years. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18:1665–1670. - PubMed
-
- Jensen JA. Breast cancer: is nipple sparing mastectomy safe? Ann Surg. 2009;250:657–658. - PubMed
-
- Crile G, Jr, Esselstyn CB, Jr, Hermann RE, Hoerr SO. Partial mastectomy for carcinoma of the breast. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1973;136:929–933. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

