Diagnostic and Prognostic Role of Serum Interleukin-6 in Malignant Transformation of Liver Cirrhosis
- PMID: 29963457
- PMCID: PMC6024044
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10018-1253
Diagnostic and Prognostic Role of Serum Interleukin-6 in Malignant Transformation of Liver Cirrhosis
Abstract
Aim: Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is still the most commonly used and the single most recommended marker in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Interleukin (IL)-6 is a circular cytokine and its role on carcinogenesis in various hematological and solid tumors is clearly documented. A combination of serum IL-6 and AFP may provide beneficial information regarding early diagnosis of HCC. In this study, the effect of plasma IL-6 level in the diagnosis of HCC was investigated.
Materials and methods: A total of 130 patients with liver cirrhosis, together with 30 control cases were enrolled in the trial. A diagnosis of HCC was present in 75 patients (57.6%) in the liver cirrhosis group. Blood samples were obtained from the enrolled study and control cases. Alpha-fetoprotein was quantified by chemiluminescent method. Plasma IL-6 levels of samples obtained at -80°C were quantified by human IL-6 BMS213/2 BMS213/2TEN kit.
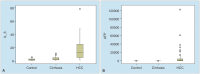
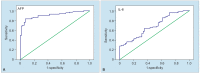
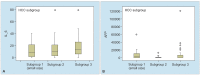
Results: The HCC patients were older than the patients in the cirrhosis group (p = 0.016). On comparison of the HCC patients with the control group, AFP (p < 0.001) and IL-6 (p < 0.001) were significantly higher among the HCC patients. Comparison of HCC patients with liver cirrhosis cases with no diagnosis of HCC revealed significantly high AFP (p < 0.001) and IL-6 levels (p < 0.001) in HCC group. Cutoff value for IL-6 was calculated as 5.73 (pg/mL). No difference was detected in AFP (p = 0.600) and IL-6 (0.344) in all three subgroups. A total of 17 patients died during a mean follow-up period of 32.9 months. No correlation was found between mean AFP values and IL-6 values and survival rates.
Conclusion: Plasma IL-6 level was found to be significant in the diagnosis of HCC. Alpha-fetoprotein and IL-6 provided no advantage in terms of early diagnosis of HCC and no correlation was observed between these markers and survival.How to cite this article: Yakut M, Özkan H, Karakaya MF, Erdal H. Diagnostic and Prognostic Role of Serum Interleukin-6 in Malignant Transformation of Liver Cirrhosis. Euroasian J Hepato-Gastroenterol 2018;8(1):23-30.
Keywords: Cirrhosis; Diagnosis; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Interleukin-6; Prognostic role..
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Surveillance: Benefit of Serum Alfa-fetoprotein in Real-world Practice.Euroasian J Hepatogastroenterol. 2018 Jan-Jun;8(1):83-87. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10018-1268. Epub 2018 May 1. Euroasian J Hepatogastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29963472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein tests for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis B-associated liver cirrhosis.Oncol Lett. 2017 May;13(5):3457-3464. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.5890. Epub 2017 Mar 22. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28521452 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of three hepatitis markers (p53 antibodies, vascular endothelial growth factors and alpha fetoprotein) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepatogastroenterology. 2009 Sep-Oct;56(94-95):1417-24. Hepatogastroenterology. 2009. PMID: 19950803
-
Assessment of the correlation between serum prolidase and alpha-fetoprotein levels in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jun 14;21(22):6999-7007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i22.6999. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26078578 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic value of alpha-fetoprotein, des-γ-carboxy prothrombin and squamous cell carcinoma antigen immunoglobulin M complexes in hepatocellular carcinoma.Minerva Med. 2011 Oct;102(5):363-71. Minerva Med. 2011. PMID: 22193346 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical and Prognostic Biomarker Value of Blood-Circulating Inflammatory Cytokines in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Oncology. 2023;101(11):730-737. doi: 10.1159/000531870. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Oncology. 2023. PMID: 37467732 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Serum Interleukin-6 Concentration on the Prognosis After Radiotherapy for Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Nov 21;2024:4696097. doi: 10.1155/cjgh/4696097. eCollection 2024. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 39619013 Free PMC article.
-
Astragali Radix Contributes to the Inhibition of Liver Fibrosis via High-Mobility Group Box 1-Mediated Inflammatory Signaling Pathway.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Mar 13;2021:5574010. doi: 10.1155/2021/5574010. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 33790974 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-6 Induced Proliferation Is Attenuated by Transforming Growth Factor-β-Induced Signaling in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells.Front Oncol. 2022 Jan 20;11:811941. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.811941. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35127527 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk network among multiple inflammatory mediators in liver fibrosis.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Sep 7;25(33):4835-4849. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i33.4835. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31543677 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Henry L, Lavabre-Bertrand T, Vercambre L, Ramos J, Carillo S, Guiraud I, Pouderoux P, Bismuth M, Valats J-C, Demattei C et al. Plasma proteasome level is a reliable early marker of malignant transformation of liver cirrhosis. Gut. 2009 Jun;58(6):833–838. - PubMed
-
- Stroffolini T. Etiological factor of hepatocellular carcinoma in Italy. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2005 Mar;51(1):1–5. - PubMed
-
- Trinchet JC, Alperovitch A, Bedossa P, Degos F, Hainaut P, Beers BV. Epidemiology, prevention, screening and diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma] Bull Cancer. 2009 Jan;96(1):35–43. - PubMed
-
- Sato Y, Nakata K, Kato Y, Shima M, Ishii N, Koji T, Taketa K, Endo Y, Nagataki S. Early recognition of hepatocellular carcinoma based on altered profiles of alpha-fetoprotein. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jun;328:1802–1806. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
