Diagnostic value of symptoms and signs for identifying urinary tract infection in older adult outpatients: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 29964141
- PMCID: PMC6203890
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jinf.2018.06.012
Diagnostic value of symptoms and signs for identifying urinary tract infection in older adult outpatients: Systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: To critically appraise and evaluate the diagnostic value of symptoms and signs in identifying UTI in older adult outpatients, using evidence from observational studies.
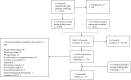
Methods: We searched Medline and Medline in process, Embase and Web of Science, from inception up to September 2017. We included studies assessing the diagnostic accuracy of symptoms and/or signs in predicting UTI in outpatients aged 65 years and above. Study quality was assessed using the QUADAS-2 tool.
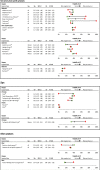
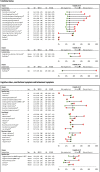
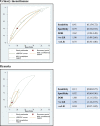
Results: We identified 15 eligible studies of variable quality, with a total of 12,039 participants (range 65-4259), and assessed the diagnostic accuracy of 66 different symptoms and signs in predicting UTI. A number of symptoms and signs typically associated with UTI, such as nocturia, urgency and abnormal vital signs, were of limited use in older adult outpatients. Inability to perform a number of acts of daily living were predictors of UTI: For example, disability in feeding oneself, + ve LR: 11.8 (95% CI 5.51-25.2) and disability in washing one's hands and face, + ve LR: 6.84 (95% CI 4.08-11.5).
Conclusions: The limited evidence of varying quality shows that a number of symptoms and signs traditionally associated with UTI may have limited diagnostic value in older adult outpatients.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Older adults; Symptoms and signs; Urinary tract infection.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures


Comment in
-
Diagnosing urinary tract infection in older people.J Infect. 2019 Apr;78(4):323-337. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2019.01.001. Epub 2019 Jan 16. J Infect. 2019. PMID: 30658079 No abstract available.
References
-
- The health and care of older people [http://www.hscic.gov.uk/catalogue/PUB14369/focu-on-hac-op-main-pub-doc%2...].
-
- Tal S, Guller V, Levi S, Bardenstein R, Berger D, Gurevich I. Profile and prognosis of febrile elderly patients with bacteremic urinary tract infection. J Infect. 2005;50(4):296–305. - PubMed
-
- The UK sepsis trust [http://sepsistrust.org].
-
- National Center for Health Statistics: Health, United States, 2014: With Special Feature on Adults Aged 55–64, National Center for Health Statistics, 2015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

