Mapping genes for drug chronotherapy
- PMID: 29964181
- PMCID: PMC6263156
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2018.06.011
Mapping genes for drug chronotherapy
Abstract
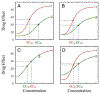
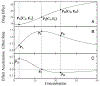
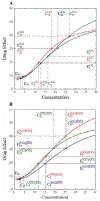
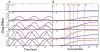
Genome-wide association studies have been increasingly used to map and characterize genes that contribute to interindividual variation in drug response. Some studies have integrated the pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) processes of drug reactions into association mapping, gleaning new insight into how genes determine the dynamic relationship of drug effect and drug dose. Here, we present an evolutionary framework by which two distinct concepts, chronopharmacodynamics and heterochrony (describing variation in the timing and rate of developmental events), are married to comprehend the pharmacogenetic architecture of drug response. The resulting new concept, heterochronopharmacodynamics (HCPD), can better interpret how genes influence drug efficacy and drug toxicity according to the circadian rhythm of the body and changes in drug concentration.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
We claimed no CONFLICTS OF INTEREST.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

