Cycling of Rational Hybridization Chain Reaction To Enable Enzyme-Free DNA-Based Clinical Diagnosis
- PMID: 29965722
- PMCID: PMC6070952
- DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.8b03183
Cycling of Rational Hybridization Chain Reaction To Enable Enzyme-Free DNA-Based Clinical Diagnosis
Abstract
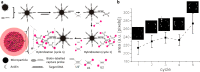
In order to combat the growing threat of global infectious diseases, there is a need for rapid diagnostic technologies that are sensitive and that can provide species specific information (as might be needed to direct therapy as resistant strains of microbes emerge). Here, we present a convenient, enzyme-free amplification mechanism for a rational hybridization chain reaction, which is implemented in a simple format for isothermal amplification and sensing, applied to the DNA-based diagnosis of hepatitis B virus (HBV) in 54 patients. During the cycled amplification process, DNA monomers self-assemble in an organized and controllable way only when a specific target HBV sequence is present. This mechanism is confirmed using super-resolution stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy. The enabled format is designed in a manner analogous to an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, generating colored products with distinct tonality and with a limit of detection of ca. five copies/reaction. This routine assay also showed excellent sensitivity (>97%) in clinical samples demonstrating the potential of this convenient, low cost, enzyme-free method for use in low resource settings.
Keywords: DNA self-assembly; HBV; cycling; diagnostic; enzyme-free; hybridization chain reaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

