Circadian variation in pulmonary inflammatory responses is independent of rhythmic glucocorticoid signaling in airway epithelial cells
- PMID: 29965797
- PMCID: PMC6355062
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.201800026RR
Circadian variation in pulmonary inflammatory responses is independent of rhythmic glucocorticoid signaling in airway epithelial cells
Abstract
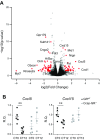
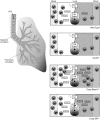
The circadian clock is a critical regulator of immune function. We recently highlighted a role for the circadian clock in a mouse model of pulmonary inflammation. The epithelial clock protein Bmal1 was required to regulate neutrophil recruitment in response to inflammatory challenge. Bmal1 regulated glucocorticoid receptor (GR) recruitment to the neutrophil chemokine, CXC chemokine ligand 5 (CXCL5), providing a candidate mechanism. We now show that clock control of pulmonary neutrophilia persists without rhythmic glucocorticoid availability. Epithelial GR-null mice had elevated expression of proinflammatory chemokines in the lung under homeostatic conditions. However, deletion of GR in the bronchial epithelium blocked rhythmic CXCL5 production, identifying GR as required to confer circadian control to CXCL5. Surprisingly, rhythmic pulmonary neutrophilia persisted, despite nonrhythmic CXCL5 responses, indicating additional circadian control mechanisms. Deletion of GR in myeloid cells alone did not prevent circadian variation in pulmonary neutrophilia and showed reduced neutrophilic inflammation in response to dexamethasone treatment. These new data show GR is required to confer circadian control to some inflammatory chemokines, but that this alone is insufficient to prevent circadian control of neutrophilic inflammation in response to inhaled LPS, with additional control mechanisms arising in the myeloid cell lineage.-Ince, L. M., Zhang, Z., Beesley, S., Vonslow, R. M., Saer, B. R., Matthews, L. C., Begley, N., Gibbs, J. E., Ray, D. W., Loudon, A. S. I. Circadian variation in pulmonary inflammatory responses is independent of rhythmic glucocorticoid signaling in airway epithelial cells.
Keywords: circadian rhythms; endocrinology; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors thank Prof. Hugh Piggins, Dr. Alun Hughes, and Dr. David Spiller for their assistance with the bioluminescence recordings of lung sections; Dr. David Bechtold for assistance with surgical techniques; Louise Hunter for technical assistance during
Figures


Similar articles
-
An epithelial circadian clock controls pulmonary inflammation and glucocorticoid action.Nat Med. 2014 Aug;20(8):919-26. doi: 10.1038/nm.3599. Epub 2014 Jul 27. Nat Med. 2014. PMID: 25064128 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide effect of pulmonary airway epithelial cell-specific Bmal1 deletion.FASEB J. 2019 May;33(5):6226-6238. doi: 10.1096/fj.201801682R. Epub 2019 Feb 22. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30794439 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E Signals via TLR4 to Induce CXCL5 Secretion by Asthmatic Airway Epithelial Cells.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2020 Aug;63(2):185-197. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2019-0209OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32338995 Free PMC article.
-
Cathelicidin is a "fire alarm", generating protective NLRP3-dependent airway epithelial cell inflammatory responses during infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Apr 12;15(4):e1007694. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007694. eCollection 2019 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30978238 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid receptor signaling in health and disease.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013 Sep;34(9):518-30. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2013.07.003. Epub 2013 Aug 14. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23953592 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Control of Leukocyte Trafficking by Stress-Associated Hormones.Front Immunol. 2019 Jan 11;9:3143. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03143. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30687335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HNF4A modulates glucocorticoid action in the liver.Cell Rep. 2022 Apr 19;39(3):110697. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110697. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 35443180 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian Regulation of the Neuroimmune Environment Across the Lifespan: From Brain Development to Aging.J Biol Rhythms. 2023 Oct;38(5):419-446. doi: 10.1177/07487304231178950. Epub 2023 Jun 26. J Biol Rhythms. 2023. PMID: 37357738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Time of Day of Vaccination Affects SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Responses in an Observational Study of Health Care Workers.J Biol Rhythms. 2022 Feb;37(1):124-129. doi: 10.1177/07487304211059315. Epub 2021 Dec 4. J Biol Rhythms. 2022. PMID: 34866459 Free PMC article.
-
Pleiotropic Effects of Glucocorticoids on the Immune System in Circadian Rhythm and Stress.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 8;12:706951. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.706951. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34691020 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mizobe K., Kishihara K., Ezz-Din El-Naggar R., Madkour G. A., Kubo C., Nomoto K. (1997) Restraint stress-induced elevation of endogenous glucocorticoid suppresses migration of granulocytes and macrophages to an inflammatory locus. J. Neuroimmunol. 73, 81–89 - PubMed
-
- Gelati M., Corsini E., De Rossi M., Masini L., Bernardi G., Massa G., Boiardi A., Salmaggi A. (2002) Methylprednisolone acts on peripheral blood mononuclear cells and endothelium in inhibiting migration phenomena in patients with multiple sclerosis. Arch. Neurol. 59, 774–780 - PubMed
-
- Gibbs J., Ince L., Matthews L., Mei J., Bell T., Yang N., Saer B., Begley N., Poolman T., Pariollaud M., Farrow S., DeMayo F., Hussell T., Worthen G. S., Ray D., Loudon A. (2014) An epithelial circadian clock controls pulmonary inflammation and glucocorticoid action. Nat. Med. 20, 919–926 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zen M., Canova M., Campana C., Bettio S., Nalotto L., Rampudda M., Ramonda R., Iaccarino L., Doria A. (2011) The kaleidoscope of glucorticoid effects on immune system. Autoimmun. Rev. 10, 305–310 - PubMed
-
- De Kloet E. R., Sarabdjitsingh R. A. (2008) Everything has rhythm: focus on glucocorticoid pulsatility. Endocrinology 149, 3241–3243 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MR/P011853/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/K015885/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/K003097/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/P023576/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 107851/Z/15/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

