Measurement Characteristics of the Knowledge Assessment of Renal Transplantation
- PMID: 29965952
- PMCID: PMC6311148
- DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000002349
Measurement Characteristics of the Knowledge Assessment of Renal Transplantation
Abstract
Background: Kidney transplant is the best treatment for most end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients, but proportionally few ESRD patients receive kidney transplant. To make an informed choice about whether to pursue kidney transplant, patients must be knowledgeable of its risks and benefits. To reliably and validly measure ESRD patients' kidney transplant knowledge, rigorously tested measures are required. This article describes the development and psychometric testing of the Knowledge Assessment of Renal Transplantation (KART).
Methods: We administered 17 transplant knowledge items to a sample of 1294 ESRD patients. Item characteristics and scale scores were estimated using an Item Response Theory graded response model. Construct validity was tested by examining differences in scale scores between patients who had spent less than 1 and 1 hour or longer receiving various types of transplant education.
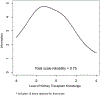
Results: Item Response Theory modeling suggested that 15 items should be retained for the KART. This scale had a marginal reliability of 0.75 and evidenced acceptable reliability (>0.70) across most of its range. Construct validity was supported by the KART's ability to distinguish patients who had spent less than 1 and 1 hour or longer receiving different types of kidney transplant education, including talking to doctors/medical staff (effect size [ES], 0.61; P < 0.001), reading brochures (ES, 0.45; P < 0.001), browsing the internet (ES, 0.56; P < 0.001), and watching videos (ES, 0.56; P < 0.001).
Conclusions: The final 15-item KART can be used to determine the kidney transplant knowledge levels of ESRD patients and plan appropriate interventions to ensure informed transplant decision making occurs.
Figures
Comment in
-
Measuring Patient Knowledge of Kidney Transplantation: An Initial Step to Close the Knowledge Gap.Transplantation. 2019 Mar;103(3):459-460. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000002350. Transplantation. 2019. PMID: 29965951 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- United States Renal Data System. 2017 USRDS annual data report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2017. DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2018.01.002. - DOI
-
- Ogutmen B, Yildirim A, Sever MS, et al. Health-Related Quality of Life After Kidney Transplantation in Comparison Intermittent Hemodialysis, Peritoneal Dialysis, and Normal Controls. Transplant Proc. 2006;38(2):419–421. - PubMed
-
- Kucirka LM, Grams ME, Balhara KS, Jaar BG, Segev DL. Disparities in provision of transplant information affect access to kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2012;12(2):351–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical