Evaluation of safety and immunogenicity of a group A streptococcus vaccine candidate (MJ8VAX) in a randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 29965967
- PMCID: PMC6028081
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198658
Evaluation of safety and immunogenicity of a group A streptococcus vaccine candidate (MJ8VAX) in a randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Group A streptococcus (GAS) is a serious human pathogen that affects people of different ages and socio-economic levels. Although vaccination is potentially one of the most effective methods to control GAS infection and its sequelae, few prototype vaccines have been investigated in humans. In this study, we report the safety and immunogenicity of a novel acetylated peptide-protein conjugate vaccine candidate MJ8VAX (J8-DT), when delivered intramuscularly to healthy adults.
Methods: A randomized, double-blinded, controlled Phase I clinical trial was conducted in 10 healthy adult participants. Participants were randomized 4:1 to receive the vaccine candidate (N = 8) or placebo (N = 2). A single dose of the vaccine candidate (MJ8VAX), contained 50 μg of peptide conjugate (J8-DT) adsorbed onto aluminium hydroxide and re-suspended in PBS in a total volume of 0.5 mL. Safety of the vaccine candidate was assessed by monitoring local and systemic adverse reactions following intramuscular administration. The immunogenicity of the vaccine was assessed by measuring the levels of peptide (anti-J8) and toxoid carrier (anti-DT)-specific antibodies in serum samples.
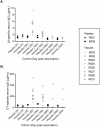
Results: No serious adverse events were reported over 12 months of study. A total of 13 adverse events (AEs) were recorded, two of which were assessed to be associated with the vaccine. Both were mild in severity. No local reactogenicity was recorded in any of the participants. MJ8VAX was shown to be immunogenic, with increase in vaccine-specific antibodies in the participants who received the vaccine. The maximum level of vaccine-specific antibodies was detected at 28 days post immunization. The level of these antibodies decreased with time during follow-up. Participants who received the vaccine also had a corresponding increase in anti-DT serum antibodies.
Conclusions: Intramuscular administration of MJ8VAX was demonstrated to be safe and immunogenic. The presence of DT in the vaccine formulation resulted in a boost in the level of anti-DT antibodies.
Trial registration: ACTRN12613000030774.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist. The company Q-Pharm Pty Ltd provides clinical trials services. Q-Pharm Pty, Ltd did not fund this study. In this study they conducted the trial as a fee for service. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
References
-
- Carapetis JR, Beaton A, Cunningham MW, Guilherme L, Karthikeyan G, Mayosi BM, et al. Acute rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2: 15084 doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2015.84 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- White AV, Hoy WE, McCredie DA. Childhood post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis as a risk factor for chronic renal disease in later life. Med J Aust. 2001;174: 492–496. - PubMed
-
- Carapetis JR. The stark reality of rheumatic heart disease. Eur Heart J. 2015;36: 1070–1073. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu507 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chang C. Cutting edge issues in rheumatic fever. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2012;42: 213–237. doi: 10.1007/s12016-011-8271-1 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Watkins DA, Johnson CO, Colquhoun SM, Karthikeyan G, Beaton A, Bukhman G, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of rheumatic heart disease, 1990–2015. N Engl J Med. 2017;377: 713–722. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1603693 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

