Chemical Structures and Biological Activities of Limonoids from the Genus Swietenia (Meliaceae)
- PMID: 29966275
- PMCID: PMC6099683
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23071588
Chemical Structures and Biological Activities of Limonoids from the Genus Swietenia (Meliaceae)
Abstract
Swietenia is a genus in the plant family Meliaceae. This genus contains seven to eight known species, found in the tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas and West Africa. Thus far, more than 160 limonoids have been isolated from four species of the genus Swietenia. Limonoids are rich in structure type and biological activity, and these compounds are the main active components in the Swietenia species. This paper will give a comprehensive overview of the recent phytochemical and pharmacological research on the terpenes from Swietenia plants and encourage further drug discovery research.
Keywords: biological activities; chemical components; genus Swietenia; limonoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
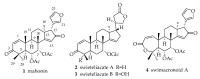

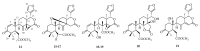




References
-
- Dutta M., Biswas U.K., Chakraborty R., Banerjee P., Raychaudhuri U. Regeneration of pancreatic β-cells on streptozotocin induced diabetic rats under the effect of swietenia macrophylla seeds. Int. J. Green Pharm. 2013;6:336–339. doi: 10.4103/0973-8258.108253. - DOI
-
- Dutta M., Biswas U.K., Chakraborty R., Banerjee P., Maji D., Mondal M.C., Raychaudhuri U. Antidiabetic and antioxidant effect of Swietenia macrophylla seeds in experimental type 2 diabetic rats. Int. J. Diabetes Dev. Ctries. 2013;33:60–65. doi: 10.1007/s13410-012-0109-8. - DOI
-
- Dewanjee S., Kundu M., Maiti A., Majumdar R., Majumdar A., Mandel S.C. In vitro evaluation of antimicrobial activity of crude extract from plants Diospyros peregrina, Coccinia grandis and Swietenia macrophylla. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2007;6:773–778. doi: 10.4314/tjpr.v6i3.14658. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

