A novel miRNA, miR-13664, targets CpCYP314A1 to regulate deltamethrin resistance in Culex pipiens pallens
- PMID: 29966536
- PMCID: PMC6318076
- DOI: 10.1017/S0031182018001002
A novel miRNA, miR-13664, targets CpCYP314A1 to regulate deltamethrin resistance in Culex pipiens pallens
Abstract
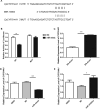
Extensive insecticide use has led to the resistance of mosquitoes to these insecticides, posing a major barrier to mosquito control. Previous Solexa high-throughput sequencing of Culex pipiens pallens in the laboratory has revealed that the abundance of a novel microRNA (miRNA), miR-13664, was higher in a deltamethrin-sensitive (DS) strain than a deltamethrin-resistant (DR) strain. Real-time quantitative PCR revealed that the miR-13664 transcript level was lower in the DR strain than in the DS strain. MiR-13664 oversupply in the DR strain increased the susceptibility of these mosquitoes to deltamethrin, whereas inhibition of miR-13664 made the DS strain more resistant to deltamethrin. Results of bioinformatic analysis, quantitative reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction, luciferase assay and miR mimic/inhibitor microinjection revealed CpCYP314A1 to be a target of miR-13664. In addition, downregulation of CpCYP314A1 expression in the DR strain reduced the resistance of mosquitoes to deltamethrin. Taken together, our results indicate that miR-13664 could regulate deltamethrin resistance by interacting with CpCYP314A1, providing new insights into mosquito resistance mechanisms.
Keywords: CpCYP314A1; Culex pipiens pallens; deltamethrin resistance; miR-13664.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



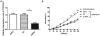
Similar articles
-
MiR-279-3p regulates deltamethrin resistance through CYP325BB1 in Culex pipiens pallens.Parasit Vectors. 2021 Oct 12;14(1):528. doi: 10.1186/s13071-021-05033-5. Parasit Vectors. 2021. PMID: 34641939 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-4448 is involved in deltamethrin resistance by targeting CYP4H31 in Culex pipiens pallens.Parasit Vectors. 2021 Mar 16;14(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s13071-021-04665-x. Parasit Vectors. 2021. PMID: 33726813 Free PMC article.
-
The role of miR-2∼13∼71 cluster in resistance to deltamethrin in Culex pipiens pallens.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2017 May;84:15-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2017.03.006. Epub 2017 Mar 23. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28342977
-
Application of deltamethrin-impregnated bednets for mosquito and malaria control in Yunnan, China.Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1996 Jun;27(2):367-71. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1996. PMID: 9280005 Review.
-
Pyrethroid resistance in Culex pipiens mosquitoes.Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2015 May;120:68-76. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2014.12.018. Epub 2014 Dec 19. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25987223 Review.
Cited by
-
Profiling of MicroRNAs in Midguts of Plutella xylostella Provides Novel Insights Into the Bacillus thuringiensis Resistance.Front Genet. 2021 Sep 8;12:739849. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.739849. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34567090 Free PMC article.
-
From Global to Local-New Insights into Features of Pyrethroid Detoxification in Vector Mosquitoes.Insects. 2021 Mar 24;12(4):276. doi: 10.3390/insects12040276. Insects. 2021. PMID: 33804964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exposure to Temperature and Insecticides Modulates the Expression of Small Noncoding RNA-Associated Transcripts in the Colorado Potato Beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae).J Insect Sci. 2022 Jan 1;22(1):23. doi: 10.1093/jisesa/ieac004. J Insect Sci. 2022. PMID: 35172010 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Coding RNAs Potentially Involved in Pyrethroid Resistance of Anopheles funestus Population in Western Kenya.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 29:rs.3.rs-3979432. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3979432/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: BMC Genomics. 2025 Jan 23;26(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11260-2. PMID: 38464038 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Aedes aegypti miRNA-33 modulates permethrin induced toxicity by regulating VGSC transcripts.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 31;11(1):7301. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86665-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33790374 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aizoun N, Aikpon R, Padonou GG, Oussou O, Oke-Agbo F, Gnanguenon V, Ossè R, Akogbeto M. Mixed-function oxidases and esterases associated with permethrin, deltamethrin and bendiocarb resistance in Anopheles gambiae s.l. in the south-north transect Benin, West Africa. Parasites & Vectors. 2013;6:223. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-6-223. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhatt S, Gething PW, Brady OJ, Messina JP, Farlow AW, Moyes CL, Drake JM, Brownstein JS, Hoen AG, Sankoh O, Myers MF, George DB, Jaenisch T, Wint GRW, Simmons CP, Scott TW, Farrar JJ, Hay SI. The global distribution and burden of dengue. Nature. 2013;496:504–507. doi: 10.1038/nature12060. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

