Overview of the Cytoskeleton from an Evolutionary Perspective
- PMID: 29967009
- PMCID: PMC6028065
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a030288
Overview of the Cytoskeleton from an Evolutionary Perspective
Abstract
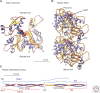
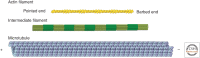
Organisms in the three domains of life depend on protein polymers to form a cytoskeleton that helps to establish their shapes, maintain their mechanical integrity, divide, and, in many cases, move. Eukaryotes have the most complex cytoskeletons, comprising three cytoskeletal polymers-actin filaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules-acted on by three families of motor proteins (myosin, kinesin, and dynein). Prokaryotes have polymers of proteins homologous to actin and tubulin but no motors, and a few bacteria have a protein related to intermediate filament proteins.
Copyright © 2018 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Derman AI, Becker EC, Truong BD, Fujioka A, Tucey TM, Erb ML, Patterson PC, Pogliano J. 2009. Phylogenetic analysis identifies many uncharacterized actin-like proteins (Alps) in bacteria: Regulated polymerization, dynamic instability and treadmilling in Alp7A. Mol Microbiol 73: 534–552. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
