Gold Nanoparticle-Conjugated Cinnamic Acid Exhibits Antiacanthamoebic and Antibacterial Properties
- PMID: 29967024
- PMCID: PMC6125513
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00630-18
Gold Nanoparticle-Conjugated Cinnamic Acid Exhibits Antiacanthamoebic and Antibacterial Properties
Abstract
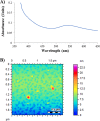
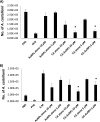
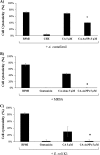
trans-Cinnamic acid (CA) is a natural organic compound. Using amoebicidal assays, for the first time we showed that CA affected the viability of the protist pathogen Acanthamoeba castellanii Conjugation with gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) enhanced the antiamoebic effects of CA. CA-coated AuNPs (CA-AuNPs) also exhibited significant excystation and encystation activity, compared to CA and AuNPs alone. Pretreatment of amoebae with CA-AuNPs inhibited A. castellanii-mediated host cell cytotoxicity. Moreover, CA-AuNPs exhibited potent effects against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and neuropathogenic Escherichia coli K1 and protected host cells against bacteria-mediated host cell death.
Keywords: Acanthamoeba; E. coli; MRSA; cinnamic acid; gold nanoparticles.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

