Recent Molecular Genetic Explorations of Caenorhabditis elegans MicroRNAs
- PMID: 29967059
- PMCID: PMC6028246
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.118.300291
Recent Molecular Genetic Explorations of Caenorhabditis elegans MicroRNAs
Abstract
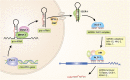
MicroRNAs are small, noncoding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level in essentially all aspects of Caenorhabditis elegans biology. More than 140 genes that encode microRNAs in C. elegans regulate development, behavior, metabolism, and responses to physiological and environmental changes. Genetic analysis of C. elegans microRNA genes continues to enhance our fundamental understanding of how microRNAs are integrated into broader gene regulatory networks to control diverse biological processes, including growth, cell division, cell fate determination, behavior, longevity, and stress responses. As many of these microRNA sequences and the related processing machinery are conserved over nearly a billion years of animal phylogeny, the assignment of their functions via worm genetics may inform the functions of their orthologs in other animals, including humans. In vivo investigations are especially important for microRNAs because in silico extrapolation of their functions using mRNA target prediction programs can easily assign microRNAs to incorrect genetic pathways. At this mezzanine level of microRNA bioinformatic sophistication, genetic analysis continues to be the gold standard for pathway assignments.
Keywords: Argonaute; Caenorhabditis elegans; WormBook; miRISC; microRNA; mutant phenotypes.
Copyright © 2018 by the Genetics Society of America.
Figures
References
-
- Abrahante J. E., Daul A. L., Li M., Volk M. L., Tennessen J. M., et al. , 2003. The Caenorhabditis elegans hunchback-like gene lin-57/hbl-1 controls developmental time and is regulated by microRNAs. Dev. Cell 4: 625–637. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

