Gene Regulation by Redox-Sensitive Burkholderia thailandensis OhrR and Its Role in Bacterial Killing of Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 29967095
- PMCID: PMC6105889
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00322-18
Gene Regulation by Redox-Sensitive Burkholderia thailandensis OhrR and Its Role in Bacterial Killing of Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
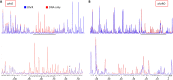
Fatty acid hydroperoxides are involved in host-pathogen interactions. In both plants and mammals, polyunsaturated fatty acids are liberated during infection and enzymatically oxidized to the corresponding toxic hydroperoxides during the defensive oxidative burst that is designed to thwart the infection. The bacterial transcription factor OhrR (organic hydroperoxide reductase regulator) is oxidized by organic hydroperoxides, as a result of which the ohr gene encoding organic hydroperoxide reductase is induced. This enzyme converts the hydroperoxides to less toxic alcohols. We show here that OhrR from Burkholderia thailandensis represses expression of ohr Gene expression is induced by cumene hydroperoxide and to a lesser extent by inorganic oxidants; however, Ohr contributes to degradation only of the organic hydroperoxide. B. thailandensis OhrR, which binds specific sites in both ohr and ohrR promoters, as evidenced by DNase I footprinting, belongs to the 2-Cys subfamily of OhrR proteins, and its oxidation leads to reversible disulfide bond formation between conserved N- and C-terminal cysteines in separate monomers. Oxidation of the N-terminal Cys is sufficient for attenuation of DNA binding in vitro, with complete restoration of DNA binding occurring on addition of a reducing agent. Surprisingly, both overexpression of ohr and deletion of ohr results in enhanced survival on exposure to organic hydroperoxide in vitro While Δohr cells are more virulent in a Caenorhabditis elegans model of infection, ΔohrR cells are less so. Taken together, our data suggest that B. thailandensis OhrR has several unconventional features and that both OhrR and organic hydroperoxides may contribute to virulence.
Keywords: DNase I footprinting; MarR; Ohr; ROS; gene regulation; organic hydroperoxide; transcription factors.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures





Similar articles
-
MarR Family Transcription Factors from Burkholderia Species: Hidden Clues to Control of Virulence-Associated Genes.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2018 Nov 28;83(1):e00039-18. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00039-18. Print 2019 Mar. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2018. PMID: 30487164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ohrR and ohr are the primary sensor/regulator and protective genes against organic hydroperoxide stress in Agrobacterium tumefaciens.J Bacteriol. 2006 Feb;188(3):842-51. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.3.842-851.2006. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16428387 Free PMC article.
-
OhrR, a transcription repressor that senses and responds to changes in organic peroxide levels in Xanthomonas campestris pv. phaseoli.Mol Microbiol. 2002 Sep;45(6):1647-54. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03116.x. Mol Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12354231
-
Analyses of the regulatory mechanism and physiological roles of Pseudomonas aeruginosa OhrR, a transcription regulator and a sensor of organic hydroperoxides.J Bacteriol. 2010 Apr;192(8):2093-101. doi: 10.1128/JB.01510-09. Epub 2010 Feb 5. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20139188 Free PMC article.
-
Ohr - OhrR, a neglected and highly efficient antioxidant system: Structure, catalysis, phylogeny, regulation, and physiological roles.Free Radic Biol Med. 2022 May 20;185:6-24. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.04.001. Epub 2022 Apr 19. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35452809 Review.
Cited by
-
MarR Family Transcription Factors from Burkholderia Species: Hidden Clues to Control of Virulence-Associated Genes.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2018 Nov 28;83(1):e00039-18. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00039-18. Print 2019 Mar. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2018. PMID: 30487164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Arsenal of Leptospira Species against Oxidants.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jun 14;12(6):1273. doi: 10.3390/antiox12061273. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platforms for the Search for New Antimicrobial Agents Using In Vivo C. elegans Models.Acta Naturae. 2024 Oct-Dec;16(4):15-26. doi: 10.32607/actanaturae.27348. Acta Naturae. 2024. PMID: 39877009 Free PMC article.
-
An EmrB multidrug efflux pump in Burkholderia thailandensis with unexpected roles in antibiotic resistance.J Biol Chem. 2019 Feb 8;294(6):1891-1903. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006638. Epub 2018 Dec 13. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30545940 Free PMC article.
-
Ohr and OhrR Are Critical for Organic Peroxide Resistance and Symbiosis in Azorhizobium caulinodans ORS571.Genes (Basel). 2020 Mar 20;11(3):335. doi: 10.3390/genes11030335. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32245101 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

