Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies
- PMID: 29967350
- PMCID: PMC6553468
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-018-0104-9
Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies
Abstract
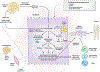
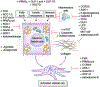
There has been a rise in the prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), paralleling a worldwide increase in diabetes and metabolic syndrome. NAFLD, a continuum of liver abnormalities from nonalcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), has a variable course but can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. Here we review the pathogenic and clinical features of NAFLD, its major comorbidities, clinical progression and risk of complications and in vitro and animal models of NAFLD enabling refinement of therapeutic targets that can accelerate drug development. We also discuss evolving principles of clinical trial design to evaluate drug efficacy and the emerging targets for drug development that involve either single agents or combination therapies intended to arrest or reverse disease progression.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and the quest for effective treatments.Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2019 Feb;8(1):77-79. doi: 10.21037/hbsn.2018.11.06. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30881974 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: does sex matter?Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2019 Apr;8(2):164-166. doi: 10.21037/hbsn.2018.12.04. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2019. PMID: 31098369 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Overview of emerging treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: more than one drug needed?Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2019 Oct;8(5):522-524. doi: 10.21037/hbsn.2019.05.08. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2019. PMID: 31673545 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Younossi ZM et al. The economic and clinical burden of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the United States and Europe. Hepatology 64, 1577–1586 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Wong RJ et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is the second leading etiology of liver disease among adults awaiting liver transplantation in the United States. Gastroenterology 148, 547–555 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

