A high-risk, Double-Hit, group of newly diagnosed myeloma identified by genomic analysis
- PMID: 29967379
- PMCID: PMC6326953
- DOI: 10.1038/s41375-018-0196-8
A high-risk, Double-Hit, group of newly diagnosed myeloma identified by genomic analysis
Abstract
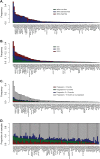
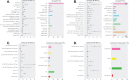
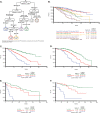
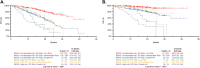
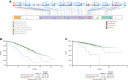
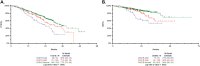
Patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (NDMM) with high-risk disease are in need of new treatment strategies to improve the outcomes. Multiple clinical, cytogenetic, or gene expression features have been used to identify high-risk patients, each of which has significant weaknesses. Inclusion of molecular features into risk stratification could resolve the current challenges. In a genome-wide analysis of the largest set of molecular and clinical data established to date from NDMM, as part of the Myeloma Genome Project, we have defined DNA drivers of aggressive clinical behavior. Whole-genome and exome data from 1273 NDMM patients identified genetic factors that contribute significantly to progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) (cumulative R2 = 18.4% and 25.2%, respectively). Integrating DNA drivers and clinical data into a Cox model using 784 patients with ISS, age, PFS, OS, and genomic data, the model has a cumlative R2 of 34.3% for PFS and 46.5% for OS. A high-risk subgroup was defined by recursive partitioning using either a) bi-allelic TP53 inactivation or b) amplification (≥4 copies) of CKS1B (1q21) on the background of International Staging System III, comprising 6.1% of the population (median PFS = 15.4 months; OS = 20.7 months) that was validated in an independent dataset. Double-Hit patients have a dire prognosis despite modern therapies and should be considered for novel therapeutic approaches.
Conflict of interest statement
Celgene Corporation: Employment, Equity Ownership: KM, FT, EF, MO, ZY, ZY, MT, and AT. Funding for data processing and storage provided by Celgene Corporation. The remaining authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
The genomic features associated with high-risk multiple myeloma.Oncotarget. 2018 Oct 26;9(84):35478-35479. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26269. eCollection 2018 Oct 26. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30464803 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Arana P, Paiva B, Cedena MT, Puig N, Cordon L, Vidriales MB, et al. Prognostic value of antigen expression in multiple myeloma: a PETHEMA/GEM study on 1,265 patients enrolled in four consecutive clinical trials. Leukemia. 2018;32:971–8. - PubMed
-
- Shah JJ, Abonour R, Gasparetto C, Hardin JW, Toomey K, Narang M, et al. Analysis of common eligibility criteria of randomized controlled trials in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients and extrapolating outcomes. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2017;17:575–83 e2. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2017.06.013. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

