Supraphysiological Levels of Oxygen Exposure During the Neonatal Period Impairs Signaling Pathways Required for Learning and Memory
- PMID: 29967535
- PMCID: PMC6028393
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-28220-4
Supraphysiological Levels of Oxygen Exposure During the Neonatal Period Impairs Signaling Pathways Required for Learning and Memory
Abstract
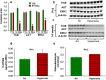
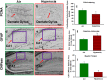
Preterm infants often require prolonged oxygen supplementation and are at high risk of neurodevelopmental impairment. We recently reported that adult mice exposed to neonatal hyperoxia (postnatal day [P] 2 to 14) had spatial navigation memory deficits associated with hippocampal shrinkage. The mechanisms by which early oxidative stress impair neurodevelopment are not known. Our objective was to identify early hyperoxia-induced alterations in hippocampal receptors and signaling pathways necessary for memory formation. We evaluated C57BL/6 mouse pups at P14, exposed to either 85% oxygen or air from P2 to 14. We performed targeted analysis of hippocampal ligand-gated ion channels and proteins necessary for memory formation, and global bioinformatic analysis of differentially expressed hippocampal genes and proteins. Hyperoxia decreased hippocampal mGLU7, TrkB, AKT, ERK2, mTORC1, RPS6, and EIF4E and increased α3, α5, and ɤ2 subunits of GABAA receptor and PTEN proteins, although changes in gene expression were not always concordant. Bioinformatic analysis indicated dysfunction in mitochondria and global protein synthesis and translational processes. In conclusion, supraphysiological oxygen exposure reduced proteins necessary for hippocampus-dependent memory formation and may adversely impact hippocampal mitochondrial function and global protein synthesis. These early hippocampal changes may account for memory deficits seen in preterm survivors following prolonged oxygen supplementation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
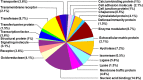
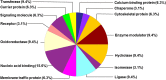
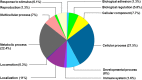
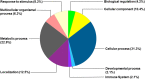
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 NS047466/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092906/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R25 NS089463/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG021612/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Aging (U.S. National Institute on Aging)/International
- R01 NS076312/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

