Synthesis, enzyme inhibitory kinetics mechanism and computational study of N-(4-methoxyphenethyl)- N-(substituted)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamides as novel therapeutic agents for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 29967717
- PMCID: PMC6025150
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.4962
Synthesis, enzyme inhibitory kinetics mechanism and computational study of N-(4-methoxyphenethyl)- N-(substituted)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamides as novel therapeutic agents for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
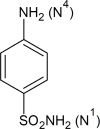
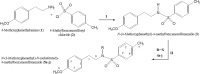
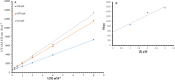
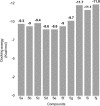
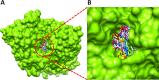
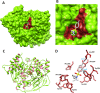
The present study comprises the synthesis of a new series of sulfonamides derived from 4-methoxyphenethylamine (1). The synthesis was initiated by the reaction of 1 with 4-methylbenzenesulfonyl chloride (2) in aqueous sodium carbonate solution at pH 9 to yield N-(4-methoxyphenethyl)-4-methylbenzensulfonamide (3).This parent molecule 3 was subsequently treated with various alkyl/aralkyl halides, (4a-j), using N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) as solvent and LiH as activator to produce a series of new N-(4-methoxyphenethyl)-N-(substituted)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamides (5a-j). The structural characterization of these derivatives was carried out by spectroscopic techniques like IR, 1H-NMR, and 13C-NMR. The elemental analysis data was also coherent with spectral data of these molecules. The inhibitory effects on acetylcholinesterase and DPPH were evaluated and it was observed that N-(4-Methoxyphenethyl)-4-methyl-N-(2-propyl)benzensulfonamide (5c) showed acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity 0.075 ± 0.001 (IC50 0.075 ± 0.001 µM) comparable to Neostigmine methylsulfate (IC50 2.038 ± 0.039 µM).The docking studies of synthesized ligands 5a-j were also carried out against acetylcholinesterase (PDBID 4PQE) to compare the binding affinities with IC50 values. The kinetic mechanism analyzed by Lineweaver-Burk plots demonstrated that compound (5c) inhibits the acetylcholinesterase competitively to form an enzyme inhibitor complex. The inhibition constants Ki calculated from Dixon plots for compound (5c) is 2.5 µM. It was also found from kinetic analysis that derivative 5c irreversible enzyme inhibitor complex. It is proposed on the basis of our investigation that title compound 5c may serve as lead structure for the design of more potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitors.
Keywords: Acetylcholinesterase; Alkyl/aralkyl halides; Molecular docking; Spectral analysis; Sulfonamides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synthesis of some new N-(alkyl/aralkyl)-N-(4-methoxyphenethyl) benzene sulfonamides as antibacterial agents against Escherichia.Pak J Pharm Sci. 2019 Sep;32(5):1957-1964. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2019. PMID: 31813858
-
Synthesis, Antioxidant and In-Silico Studies of Potent Urease Inhibitors: N-(4-{[(4-Methoxyphenethyl)-(substituted)amino]sulfonyl}phenyl)acetamides.Drug Res (Stuttg). 2019 Feb;69(2):111-120. doi: 10.1055/a-0654-5074. Epub 2018 Aug 7. Drug Res (Stuttg). 2019. PMID: 30086567
-
Design, synthesis, kinetic mechanism and molecular docking studies of novel 1-pentanoyl-3-arylthioureas as inhibitors of mushroom tyrosinase and free radical scavengers.Eur J Med Chem. 2017 Dec 1;141:273-281. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.09.059. Epub 2017 Sep 29. Eur J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 29040952
-
Synthesis, Antibacterial and Lipoxygenase Inhibition Studies of N-(Alkyl/aralkyl)-N-(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-6-yl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamides.Turk J Pharm Sci. 2017 Apr;14(1):49-55. doi: 10.4274/tjps.84756. Epub 2017 Apr 15. Turk J Pharm Sci. 2017. PMID: 32454594 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of elastase inhibiting novel ethylated thiazole-triazole acetamide hybrids: Mechanistic insights through kinetics and computational contemplations.Bioorg Chem. 2019 May;86:197-209. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.01.040. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Bioorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 30711702 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of cholinesterases inhibitors from flavonoids derivatives for possible treatment of Alzheimer's disease: In silico and in vitro approaches.Curr Res Struct Biol. 2024 Apr 25;7:100146. doi: 10.1016/j.crstbi.2024.100146. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Struct Biol. 2024. PMID: 38707547 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbasi MA, Ahmad S, Aziz-ur- Rehman, Rasool S, Khan KM, Ashraf M, Nasar R, Ismail T. Sulfonamide derivatives of 2-amino-1-phenylethane as suitable cholinesterase inhibitors. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. 2014b;13:739–745. doi: 10.4314/tjpr.v13i5.13. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

