Complex characterization of oat (Avena sativa L.) lines obtained by wide crossing with maize (Zea mays L.)
- PMID: 29967749
- PMCID: PMC6022724
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.5107
Complex characterization of oat (Avena sativa L.) lines obtained by wide crossing with maize (Zea mays L.)
Abstract
Background: The oat × maize addition (OMA) lines are used for mapping of the maize genome, the studies of centromere-specific histone (CENH3), gene expression, meiotic chromosome behavior and also for introducing maize C4 photosynthetic system to oat. The aim of our study was the identification and molecular-cytogenetic characterization of oat × maize hybrids.
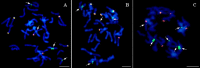
Methods: Oat DH lines and oat × maize hybrids were obtained using the wide crossing of Avena sativa L. with Zea mays L. The plants identified as having a Grande-1 retrotransposon fragment, which produced seeds, were used for genomic in situ hybridization (GISH).
Results: A total of 138 oat lines obtained by crossing of 2,314 oat plants from 80 genotypes with maize cv. Waza were tested for the presence of maize chromosomes. The presence of maize chromatin was indicated in 66 lines by amplification of the PCR product (500 bp) generated using primers specific for the maize retrotransposon Grande-1. Genomic in situ hybridization (GISH) detected whole maize chromosomes in eight lines (40%). All of the analyzed plants possessed full complement of oat chromosomes. The number of maize chromosomes differed between the OMA lines. Four OMA lines possessed two maize chromosomes similar in size, three OMA-one maize chromosome, and one OMA-four maize chromosomes. In most of the lines, the detected chromosomes were labeled uniformly. The presence of six 45S rDNA loci was detected in oat chromosomes, but none of the added maize chromosomes in any of the lines carried 45S rDNA locus. Twenty of the analyzed lines did not possess whole maize chromosomes, but the introgression of maize chromatin in the oat chromosomes. Five of 66 hybrids were shorter in height, grassy type without panicles. Twenty-seven OMA lines were fertile and produced seeds ranging in number from 1-102 (in total 613). Sixty-three fertile DH lines, out of 72 which did not have an addition of maize chromosomes or chromatin, produced seeds in the range of 1-343 (in total 3,758). Obtained DH and OMA lines were fertile and produced seeds.
Discussion: In wide hybridization of oat with maize, the complete or incomplete chromosomes elimination of maize occur. Hybrids of oat and maize had a complete set of oat chromosomes without maize chromosomes, and a complete set of oat chromosomes with one to four retained maize chromosomes.
Keywords: Doubled haploids (DH); Fertility; Genomic in situ hybridization (GISH); Oat × maize hybrids.
Conflict of interest statement
Zygmunt Nita and Krystyna Werwińska are employed by Plant Breeding Strzelce Ltd., PBAI Group.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparative characteristics of oat doubled haploids and oat × maize addition lines: Anatomical features of the leaves, chlorophyll a fluorescence and yield parameters.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 9;19(4):e0298072. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298072. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38593116 Free PMC article.
-
Addition of individual chromosomes of maize inbreds B73 and Mo17 to oat cultivars Starter and Sun II: maize chromosome retention, transmission, and plant phenotype.Theor Appl Genet. 2009 Nov;119(7):1255-64. doi: 10.1007/s00122-009-1130-2. Epub 2009 Aug 26. Theor Appl Genet. 2009. PMID: 19707741
-
Cytological and molecular characterization of oat x maize partial hybrids.Theor Appl Genet. 1996 Jul;93(1-2):123-35. doi: 10.1007/BF00225737. Theor Appl Genet. 1996. PMID: 24162209
-
Complex structure of knobs and centromeric regions in maize chromosomes.Tsitol Genet. 2000 Mar-Apr;34(2):11-5. Tsitol Genet. 2000. PMID: 10857197 Review.
-
Maize In Planta Haploid Inducer Lines: A Cornerstone for Doubled Haploid Technology.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2288:25-48. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1335-1_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34270003 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-rolling flag leaves use an effective mechanism to reduce water loss and light-induced damage under drought stress.Ann Bot. 2022 Sep 19;130(3):393-408. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcac035. Ann Bot. 2022. PMID: 35294964 Free PMC article.
-
Embryo Rescue in Plant Breeding.Plants (Basel). 2023 Aug 29;12(17):3106. doi: 10.3390/plants12173106. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37687352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3-D Nucleus Architecture in Oat × Maize Addition Lines.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 16;21(12):4280. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124280. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32560105 Free PMC article.
-
Functioning of the Photosynthetic Apparatus in Response to Drought Stress in Oat × Maize Addition Lines.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 22;21(18):6958. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186958. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32971899 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative characteristics of oat doubled haploids and oat × maize addition lines: Anatomical features of the leaves, chlorophyll a fluorescence and yield parameters.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 9;19(4):e0298072. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298072. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38593116 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barclay IR. High frequencies of haploid production in wheat (Triticum aestivum) by chromosome elimination. Nature. 1975;256:410–411. doi: 10.1038/256410a0. - DOI
-
- Bass HW, Riera-Lizarazu O, Ananiev EV, Bordoli SJ, Rines HW, Phillips RL, Sedat JW, Agard DA, Cande WZ. Evidence for the coincident initiation of homolog pairing and synapsis during the telomere-clustering (bouquet) stage of meiotic prophase. Journal of Cell Science. 2000;113:1033–1042. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhary HK, Tayeng T, Kaila V, Rather SA. Use of asynchrony in flowering for easy and economical polyhaploid induction in wheat following Imperata cylindrica—mediated chromosome elimination approach. Plant Breeding. 2013;132(2):155–158. doi: 10.1111/pbr.12036. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

