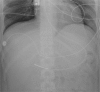
The Placement of Post-pyloric Feeding Tubes Using DRX-Revolution Mobile X-Ray System in an ICU. A Case Series
- PMID: 29967851
- PMCID: PMC5953245
- DOI: 10.1515/jccm-2016-0022
The Placement of Post-pyloric Feeding Tubes Using DRX-Revolution Mobile X-Ray System in an ICU. A Case Series
Abstract
Enteral nutrition is crucial for ensuring that critically ill patients have a proper intake of food, water, and medicine. Methods to ensure this requirement should be initiated as early as possible. The use of PPF has several advantages compared to the use of a nasogastric feeding tube. In the present paper, the cases of three critically ill patients with a nonfunctional gastrointestinal system on admission to ICU, are detailed. Enteral feeding through a nasogastric tube by prokinetic agent therapy had been unsuccessful. The bedside placement of a post-pyloric feeding tube by the DRX-Revolution X-ray system is described.
Keywords: DRX-Revolution X-ray system; enteral nutrition; post-pyloric feeding tube (PPF).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None declared
Figures
References
-
- Swinton F, Donovan K, White N.. Insertion of post-pyloric feeding tubes in the ICU is not as difficult as we thought. Journal of Intensive Care Society. 2009(10):273–4.
-
- Kearns J, Chin D, Mueller L. et al. The incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia and success in nutrient delivery with gastric versus small intestinal feeding: a randomized clinical trial. Crit Care Med. 2000;28:1742–6. - PubMed
-
- Montejo JC, Grau T, Acosta J. et al. Multicenter, prospective, randomized, single-blind study comparing the efficacy and gastrointestinal complications of early jejunal feeding with early gastric feeding in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med. 2002(30):796–800. - PubMed
-
- Stone SJ, Pickett JD, Jesurum JT.. Bedside placement of postpyloric feeding tubes. AACN Clin Issues. 2000(11):517–30. - PubMed
-
- Lenart S, Polissar NL.. Comparison of 2 methods for postpyloric placement of enteral feeding tubes. Am J Crit Care. 2003;12:357–60. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources