Use of Transcranial Doppler in Intensive Care Unit
- PMID: 29967879
- PMCID: PMC5769900
- DOI: 10.1515/jccm-2017-0021
Use of Transcranial Doppler in Intensive Care Unit
Abstract
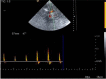
Use of transcranial Doppler has undergone much development since its introduction in 1982, making the technique suitable for general use in intensive care units. The main application in intensive care units is to assess intracranial pressure, confirm the lack of cerebral circulation in brain death, detect vasospasm in subarachnoid haemorrhage, and monitor the blood flow parameters during thrombolysis and carotid endarterectomy, as well as measuring stenosis of the main intracranial arteries in sickle cell disease in children. This review summarises the use of transcranial Doppler in intensive care units.
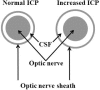
Keywords: brain death; endarterectomy; intensive care unit; intracranial pressure; optic nerve sheath diameter; sickle cell disease; subarachnoid haemorrhage; thrombolysis; transcranial Doppler; vasospasm.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Aaslid R, Markwalder TM, Nornes H.. Noninvasive transcranial Doppler ultrasound recording of flow velocity in basal cerebral arteries. J Neurosurg. 1982;57:769–74. - PubMed
-
- Lindegaard KF, Bakke SJ, Sorteberg W, Nakstad P, Nornes H.. A non-invasive Doppler ultrasound method for the evaluation of patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Radiol Suppl. 1986;369:96–8. - PubMed
-
- George MS. Neuroactivation and Neuroimaging with SPECT. Springer-Verlag; New York: 1991.
-
- Holman BL, Devous MD.. Functional brain SPECT: the emergence of a powerful clinical method. J Nucl Med. 1992;33:1888–904. - PubMed
-
- Lindegaard KF, Bakke SJ, Grolimund P, Aaslid R, Huber P, Nornes H.. Assessment of intracranial hemodynamics in carotid artery disease by transcranial Doppler ultrasound. J Neurosurg. 1985;63:890–8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
