The Oomycete Pythium oligandrum Can Suppress and Kill the Causative Agents of Dermatophytoses
- PMID: 29967972
- PMCID: PMC6156753
- DOI: 10.1007/s11046-018-0277-2
The Oomycete Pythium oligandrum Can Suppress and Kill the Causative Agents of Dermatophytoses
Abstract
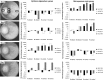
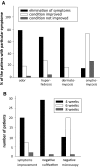
Pythium oligandrum (Oomycota) is known for its strong mycoparasitism against more than 50 fungal and oomycete species. However, the ability of this oomycete to suppress and kill the causal agents of dermatophytoses is yet to be studied. We provide a complex study of the interactions between P. oligandrum and dermatophytes representing all species dominating in the developed countries. We assessed its biocidal potential by performing growth tests, on both solid and liquid cultivation media and by conducting a pilot clinical study. In addition, we studied the molecular background of mycoparasitism using expression profiles of genes responsible for the attack on the side of P. oligandrum and the stress response on the side of Microsporum canis. We showed that dermatophytes are efficiently suppressed or killed by P. oligandrum in the artificial conditions of cultivations media between 48 and 72 h after first contact. Significant intra- and interspecies variability was noted. Of the 69 patients included in the acute regimen study, symptoms were completely eliminated in 79% of the patients suffering from foot odour, hyperhidrosis disappeared in 67% of cases, clinical signs of dermatomycoses could no longer be observed in 83% of patients, and 15% of persons were relieved of symptoms of onychomycosis. Our investigations provide clear evidence that the oomycete is able to recognize and kill dermatophytes using recognition mechanisms that resemble those described in oomycetes attacking fungi infecting plants, albeit with some notable differences.
Keywords: Aggressivity genes; Dermatophytes; Microsporum; Mycoparasitism; Pythium oligandrum; Trichophyton.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
Martin Suchánek and Radim Klimeš are owners and stakeholders in the companies Biopreparáty and Bio Agens Research and Development manufacturing biological antifungal products based on
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animals
For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Figures




References
-
- Drake LA, Dinehart SM, Farmer ER, Goltz RW, Graham GF, Hordinsky MK, et al. Guidelines of care for superficial mycotic infections of the skin: tinea corporis, tinea cruris, tinea faciei, tinea manuum, and tinea pedis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;34:282–286. doi: 10.1016/S0190-9622(96)80135-6. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

