Molecular Detection of Streptococcus pyogenes by Strand Invasion Based Amplification Assay
- PMID: 29967988
- PMCID: PMC7099210
- DOI: 10.1007/s40291-018-0346-8
Molecular Detection of Streptococcus pyogenes by Strand Invasion Based Amplification Assay
Abstract
Introduction: Streptococcus pyogenes (group A Streptococcus, GAS) is responsible for a variety of highly communicable infections, accounting for 5-15 and 20-30% of sore throat hospital visits in adults and children, respectively. Prompt diagnosis of GAS can improve the quality of patient care and minimize the unnecessary use of antibiotics.
Objective: Our objective was to develop an alternative nucleic acid amplification method for the diagnosis of GAS.
Method: We developed and evaluated a strand invasion based amplification (SIBA) assay to rapidly and specifically detect GAS. The performance of the developed GAS SIBA assay was compared with an established GAS polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay.
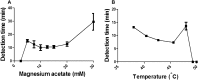
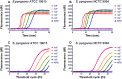
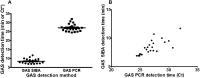
Results: The GAS SIBA assay detected small amounts (ten copies) of S. pyogenes DNA within 13 min. The rapid detection time was achieved in part by optimization of magnesium concentration and reaction temperature. The sensitivity and specificity of the GAS SIBA assay for detection of S. pyogenes from clinical specimens were both 100%, and clinical specimens were detected within ~ 8 min of starting the reaction.
Conclusion: Because the GAS SIBA assay is performed at low and constant temperature, it can be used both in centralized laboratories and for point-of-care testing. Furthermore, given its short detection time and strong analytical performance, the GAS SIBA assay could help to improve patient care and minimize unnecessary prescription of antibiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
SE, JO, SH, PA, and KE are employees of Orion Diagnostica Oy. All SIBA patents and patent applications are owned by Orion Diagnostica Oy. KE and SE are named as inventors on patents and patent applications.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Detection of Group A Streptococcus in Pharyngeal Swab Specimens by Use of the AmpliVue GAS Isothermal Helicase-Dependent Amplification Assay.J Clin Microbiol. 2015 Jul;53(7):2365-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01085-15. Epub 2015 May 13. J Clin Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25972419 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of human rhinoviruses by reverse transcription strand invasion based amplification method (RT-SIBA).J Virol Methods. 2019 Jan;263:75-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2018.10.015. Epub 2018 Oct 19. J Virol Methods. 2019. PMID: 30347198 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Streptococcus pyogenes using rapid visual molecular assay.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2015 Sep;362(18):fnv148. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnv148. Epub 2015 Aug 27. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2015. PMID: 26319025
-
[Genome of group A Streptococcus].Nihon Rinsho. 2003 Mar;61 Suppl 3:665-9. Nihon Rinsho. 2003. PMID: 12718045 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Peritonsillar abscess: clinical aspects of microbiology, risk factors, and the association with parapharyngeal abscess.Dan Med J. 2017 Mar;64(3):B5333. Dan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28260599 Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 detection using reverse transcription strand invasion based amplification and a portable compact size instrument.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 15;11(1):22214. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-01744-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34782681 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication of a Microfluidic Test Device with a 3D Printer and Its Combination with the Loop Mediated Isothermal Amplification Method to Detect Streptococcus pyogenes.Micromachines (Basel). 2024 Mar 7;15(3):365. doi: 10.3390/mi15030365. Micromachines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38542612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shulman ST, Bisno AL, Clegg HW, Gerber MA, Kaplan EL, Lee G, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and management of group A streptococcal pharyngitis: 2012 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;55(10):e86–e102. doi: 10.1093/cid/cis629. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

