CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene knockout reveals a guardian role of NF-κB/RelA in maintaining the homeostasis of human vascular cells
- PMID: 29968158
- PMCID: PMC6208479
- DOI: 10.1007/s13238-018-0560-5
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene knockout reveals a guardian role of NF-κB/RelA in maintaining the homeostasis of human vascular cells
Erratum in
-
Correction to: CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene knockout reveals a guardian role of NF-κB/RelA in maintaining the homeostasis of human vascular cells.Protein Cell. 2025 Feb 20:pwaf009. doi: 10.1093/procel/pwaf009. Online ahead of print. Protein Cell. 2025. PMID: 39977441 No abstract available.
Abstract
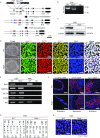
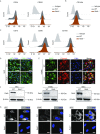
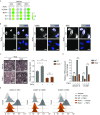
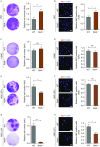
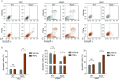
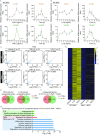
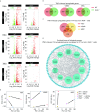
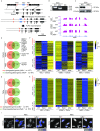
Vascular cell functionality is critical to blood vessel homeostasis. Constitutive NF-κB activation in vascular cells results in chronic vascular inflammation, leading to various cardiovascular diseases. However, how NF-κB regulates human blood vessel homeostasis remains largely elusive. Here, using CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing, we generated RelA knockout human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) and differentiated them into various vascular cell derivatives to study how NF-κB modulates human vascular cells under basal and inflammatory conditions. Multi-dimensional phenotypic assessments and transcriptomic analyses revealed that RelA deficiency affected vascular cells via modulating inflammation, survival, vasculogenesis, cell differentiation and extracellular matrix organization in a cell type-specific manner under basal condition, and that RelA protected vascular cells against apoptosis and modulated vascular inflammatory response upon tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) stimulation. Lastly, further evaluation of gene expression patterns in IκBα knockout vascular cells demonstrated that IκBα acted largely independent of RelA signaling. Taken together, our data reveal a protective role of NF-κB/RelA in modulating human blood vessel homeostasis and map the human vascular transcriptomic landscapes for the discovery of novel therapeutic targets.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Inflammation; NF-κB; RelA; Stem cell.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Actin networks modulate heterogeneous NF-κB dynamics in response to TNFα.Elife. 2024 Aug 7;13:e86042. doi: 10.7554/eLife.86042. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39110005 Free PMC article.
-
RELA governs a network of islet-specific metabolic genes necessary for beta cell function.Diabetologia. 2023 Aug;66(8):1516-1531. doi: 10.1007/s00125-023-05931-6. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Diabetologia. 2023. PMID: 37311878 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of IκBα activates RelA to reduce acute pancreatitis in mice through up-regulation of Spi2A.Gastroenterology. 2013 Jan;144(1):192-201. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.09.058. Epub 2012 Oct 3. Gastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23041330
-
The Transcription Factor NF-κB in Stem Cells and Development.Cells. 2021 Aug 10;10(8):2042. doi: 10.3390/cells10082042. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the Relationship between Nucleolar Stress and the NF-κB Pathway.Trends Genet. 2019 Oct;35(10):768-780. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2019.07.009. Epub 2019 Aug 19. Trends Genet. 2019. PMID: 31434627 Review.
Cited by
-
A bibliometric analysis of studies related to the nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway in knee osteoarthritis between 2004 and 2023.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 25;12:1572161. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1572161. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40636390 Free PMC article.
-
Osmolar Modulation Drives Reversible Cell Cycle Exit and Human Pluripotent Cell Differentiation via NF-κВ and WNT Signaling.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Feb;11(7):e2307554. doi: 10.1002/advs.202307554. Epub 2023 Dec 1. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38037844 Free PMC article.
-
Telomere-dependent and telomere-independent roles of RAP1 in regulating human stem cell homeostasis.Protein Cell. 2019 Sep;10(9):649-667. doi: 10.1007/s13238-019-0610-7. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Protein Cell. 2019. PMID: 30796637 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical screen identifies a geroprotective role of quercetin in premature aging.Protein Cell. 2019 Jun;10(6):417-435. doi: 10.1007/s13238-018-0567-y. Epub 2018 Aug 1. Protein Cell. 2019. PMID: 30069858 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT7 antagonizes human stem cell aging as a heterochromatin stabilizer.Protein Cell. 2020 Jul;11(7):483-504. doi: 10.1007/s13238-020-00728-4. Epub 2020 Jun 6. Protein Cell. 2020. PMID: 32504224 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Breitbach M, Kimura K, Luis TC, Fuegemann CJ, Woll PS, Hesse M, Facchini R, Rieck S, Jobin K, Reinhardt J, et al. In Vivo Labeling by CD73 Marks Multipotent Stromal Cells and Highlights Endothelial Heterogeneity in the Bone Marrow Niche. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;22(262–276):e267. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

