Multimodality Imaging Agents with PET as the Fundamental Pillar
- PMID: 29968300
- PMCID: PMC6314921
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.201806853
Multimodality Imaging Agents with PET as the Fundamental Pillar
Abstract
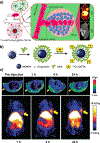
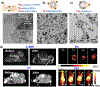
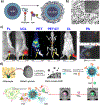
Positron emission tomography (PET) provides quantitative information in vivo with ultra-high sensitivity but is limited by its relatively low spatial resolution. Therefore, PET has been combined with other imaging modalities, and commercial systems such as PET/computed tomography (CT) and PET/magnetic resonance (MR) have become available. Inspired by the emerging field of nanomedicine, many PET-based multimodality nanoparticle imaging agents have been developed in recent years. This Minireview highlights recent progress in the design of PET-based multimodality imaging nanoprobes with an aim to overview the major advances and key challenges in this field and substantially improve our knowledge of this fertile research area.
Keywords: PET; dual-modality imaging; imaging agents; multimodality imaging; nanomedicine.
© 2019 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Multimodality imaging of nanoparticle-based vaccines: Shedding light on immunology.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2022 Sep;14(5):e1807. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1807. Epub 2022 May 2. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35501142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticle-based multimodal PET/MRI probes.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015;10(8):1343-59. doi: 10.2217/nnm.14.224. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015. PMID: 25955127 Review.
-
PET-MR and SPECT-MR multimodality probes: Development and challenges.Theranostics. 2018 Nov 29;8(22):6210-6232. doi: 10.7150/thno.26610. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 30613293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gadolinium oxide nanoparticles as potential multimodal imaging and therapeutic agents.Curr Top Med Chem. 2013;13(4):422-33. doi: 10.2174/1568026611313040003. Curr Top Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23432005 Review.
-
PET/MR: a paradigm shift.Cancer Imaging. 2013 Feb 27;13(1):36-52. doi: 10.1102/1470-7330.2013.0005. Cancer Imaging. 2013. PMID: 23446110 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NIR-II Fluorescent Probes for Fluorescence-Imaging-Guided Tumor Surgery.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 May 30;14(6):282. doi: 10.3390/bios14060282. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38920586 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A "Missile-Detonation" Strategy to Precisely Supply and Efficiently Amplify Cerenkov Radiation Energy for Cancer Theranostics.Adv Mater. 2019 Dec;31(52):e1904894. doi: 10.1002/adma.201904894. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Adv Mater. 2019. PMID: 31709622 Free PMC article.
-
The bright future of nanotechnology in lymphatic system imaging and imaging-guided surgery.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Jan 6;20(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-01232-5. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 34991595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing Biomarker Activatable Probes for Early Stratification and Timely Assessment of Therapeutic Efficacy in Cancer.Exploration (Beijing). 2025 Mar 6;5(3):20240037. doi: 10.1002/EXP.20240037. eCollection 2025 Jun. Exploration (Beijing). 2025. PMID: 40585764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bright red aggregation-induced emission nanoparticles for multifunctional applications in cancer therapy.Chem Sci. 2020 Jan 29;11(9):2369-2374. doi: 10.1039/c9sc06310b. Chem Sci. 2020. PMID: 34084398 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Judenhofer MS, Wehrl HF, Newport DF, Catana C, Siegel SB, Becker M, Thielscher A, Kneilling M, Lichy MP, Eichner M, Klingel K, Reischl G, Widmaier S, Rocken M, Nutt RE, Machulla H-J, Uludag K, Cherry SR, Claussen CD, Pichler BJ, Nat. Med 2008, 14, 459–465. - PubMed
-
- Delso G, Furst S, Jakoby B, Ladebeck R, Ganter C, Nekolla SG, Schwaiger M, Ziegler SI, J. Nucl. Med 2011, 52, 1914–1922. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

