Mitochondrial function in the heart: the insight into mechanisms and therapeutic potentials
- PMID: 29968316
- PMCID: PMC6887906
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.14431
Mitochondrial function in the heart: the insight into mechanisms and therapeutic potentials
Abstract
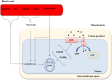
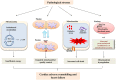
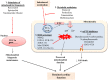
Mitochondrial dysfunction is considered as a crucial contributory factor in cardiac pathology. This has highlighted the therapeutic potential of targeting mitochondria to prevent or treat cardiac disease. Mitochondrial dysfunction is associated with aberrant electron transport chain activity, reduced ATP production, an abnormal shift in metabolic substrates, ROS overproduction and impaired mitochondrial dynamics. This review will cover the mitochondrial functions and how they are altered in various disease conditions. Furthermore, the mechanisms that lead to mitochondrial defects and the protective mechanisms that prevent mitochondrial damage will be discussed. Finally, potential mitochondrial targets for novel therapeutic intervention will be explored. We will highlight the development of small molecules that target mitochondria from different perspectives and their current progress in clinical trials. LINKED ARTICLES: This article is part of a themed section on Mitochondrial Pharmacology: Featured Mechanisms and Approaches for Therapy Translation. To view the other articles in this section visit http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bph.v176.22/issuetoc.
© 2018 The University of Manchester. British Journal of Pharmacology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Akimoto T, Pohnert SC, Li P, Zhang M, Gumbs C, Rosenberg PB et al (2005). Exercise stimulates Pgc‐1α transcription in skeletal muscle through activation of the p38 MAPK pathway. J Biol Chem. American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 280: 19587–19593. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

