Broad-Spectrum and Personalized Guide RNAs for CRISPR/Cas9 HIV-1 Therapeutics
- PMID: 29968495
- PMCID: PMC6238604
- DOI: 10.1089/AID.2017.0274
Broad-Spectrum and Personalized Guide RNAs for CRISPR/Cas9 HIV-1 Therapeutics
Abstract
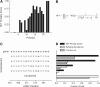
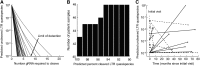
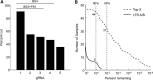
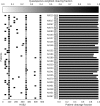
The clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)-associated Cas9 system has been used to excise the HIV-1 proviral genome from latently infected cells, potentially offering a cure for HIV-infected patients. Recent studies have shown that most published HIV-1 guide RNAs (gRNAs) do not account for the diverse viral quasispecies within or among patients, which continue to diversify with time even in long-term antiretroviral therapy (ART)-suppressed patients. Given this observation, proviral genomes were deep sequenced from 23 HIV-1-infected patients in the Drexel Medicine CNS AIDS Research and Eradication Study cohort at two different visits. Based on the spectrum of integrated proviral DNA polymorphisms observed, three gRNA design strategies were explored: based on the patient's own HIV-1 sequences (personalized), based on consensus sequences from a large sample of patients [broad-spectrum (BS)], or a combination of both approaches. Using a bioinformatic algorithm, the personalized gRNA design was predicted to cut 46 of 48 patient samples at 90% efficiency, whereas the top 4 BS gRNAs (BS4) were predicted to excise provirus from 44 of 48 patient samples with 90% efficiency. Using a mixed design with the top three BS gRNAs plus one personalized gRNA (BS3 + PS1) resulted in predicted excision of provirus from 45 of 48 patient samples with 90% efficiency. In summary, these studies used an algorithmic design strategy to identify potential BS gRNAs to target a spectrum of HIV-1 long teriminal repeat (LTR) quasispecies for use with a small HIV-1-infected population. This approach should advance CRISPR/Cas9 excision technology taking into account the extensive molecular heterogeneity of HIV-1 that persists in situ after prolonged ART.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; HIV-1; excision; gRNA; gRNA pipeline; patient-derived sequence.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel gRNA design pipeline to develop broad-spectrum CRISPR/Cas9 gRNAs for safe targeting of the HIV-1 quasispecies in patients.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 19;9(1):17088. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52353-9. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31745112 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Therapy with CRISPR/Cas9 Coming to Age for HIV Cure.AIDS Rev. 2017 Oct-Dec;19(3):167-172. AIDS Rev. 2017. PMID: 29019352
-
Designing broad-spectrum anti-HIV-1 gRNAs to target patient-derived variants.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 31;7(1):14413. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12612-z. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29089503 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR-CAS Replacing Antiviral Drugs against HIV: An Update.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2020;30(1):77-83. doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2020028233. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2020. PMID: 32421986 Review.
-
CRISPR/Cas9: a tool to eradicate HIV-1.AIDS Res Ther. 2022 Dec 1;19(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12981-022-00483-y. AIDS Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 36457057 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting and Understanding HIV Latency: The CRISPR System against the Provirus.Pathogens. 2021 Sep 28;10(10):1257. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10101257. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34684206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delivering CRISPR to the HIV-1 reservoirs.Front Microbiol. 2024 May 15;15:1393974. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1393974. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38812680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transient CRISPR-Cas Treatment Can Prevent Reactivation of HIV-1 Replication in a Latently Infected T-Cell Line.Viruses. 2021 Dec 8;13(12):2461. doi: 10.3390/v13122461. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34960730 Free PMC article.
-
Off-Target Analysis in Gene Editing and Applications for Clinical Translation of CRISPR/Cas9 in HIV-1 Therapy.Front Genome Ed. 2021 Aug 17;3:673022. doi: 10.3389/fgeed.2021.673022. eCollection 2021. Front Genome Ed. 2021. PMID: 34713260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elimination of infectious HIV DNA by CRISPR-Cas9.Curr Opin Virol. 2019 Oct;38:81-88. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2019.07.001. Epub 2019 Aug 23. Curr Opin Virol. 2019. PMID: 31450074 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

