Improved recovery time and sensitivity to H2 and NH3 at room temperature with SnOx vertical nanopillars on ITO
- PMID: 29968779
- PMCID: PMC6030158
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-28298-w
Improved recovery time and sensitivity to H2 and NH3 at room temperature with SnOx vertical nanopillars on ITO
Abstract
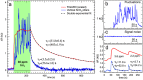
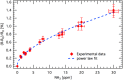
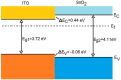
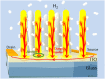
Nanostructured SnO2 is a promising material for the scalable production of portable gas sensors. To fully exploit their potential, these gas sensors need a faster recovery rate and higher sensitivity at room temperature than the current state of the art. Here we demonstrate a chemiresistive gas sensor based on vertical SnOx nanopillars, capable of sensing < 5 ppm of H2 at room temperature and 10 ppt at 230 °C. We test the sample both in vacuum and in air and observe an exceptional improvement in the performance compared to commercially available gas sensors. In particular, the recovery time for sensing NH3 at room temperature is more than one order of magnitude faster than a commercial SnO2 sensor. The sensor shows an unique combination of high sensitivity and fast recovery time, matching the requirements on materials expected to foster widespread use of portable and affordable gas sensors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Dutta S. A review on production, storage of hydrogen and its utilization as an energy resource. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014;20:1148–1156. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2013.07.037. - DOI
-
- Andio, M. Sensor Array Devices Utilizing Nano-structured Metal-oxides for Hazardous Gas Detection, Ph.D thesis, The Ohio State University (2012).
-
- Righettoni M, Amann A, Pratsinis S. Breath analysis by nanostructured metal oxides as chemo-resistive gas sensors. Mater. Today. 2015;18:163–171. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2014.08.017. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

