Synovial Fluid Metabolites Differentiate between Septic and Nonseptic Joint Pathologies
- PMID: 29969035
- PMCID: PMC6092013
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00190
Synovial Fluid Metabolites Differentiate between Septic and Nonseptic Joint Pathologies
Abstract
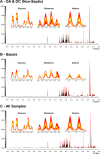
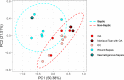
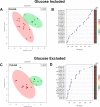
Osteoarthritis (OA), osteochondrosis (OC), and synovial sepsis in horses cause loss of function and pain. Reliable biomarkers are required to achieve accurate and rapid diagnosis, with synovial fluid (SF) holding a unique source of biochemical information. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy allows global metabolite analysis of a small volume of SF, with minimal sample preprocessing using a noninvasive and nondestructive method. Equine SF metabolic profiles from both nonseptic joints (OA and OC) and septic joints were analyzed using 1D 1H NMR spectroscopy. Univariate and multivariate statistical analyses were used to identify differential metabolite abundance between groups. Metabolites were annotated via 1H NMR using 1D NMR identification software Chenomx, with identities confirmed using 1D 1H and 2D 1H 13C NMR. Multivariate analysis identified separation between septic and nonseptic groups. Acetate, alanine, citrate, creatine phosphate, creatinine, glucose, glutamate, glutamine, glycine, phenylalanine, pyruvate, and valine were higher in the nonseptic group, while glycylproline was higher in sepsis. Multivariate separation was primarily driven by glucose; however, partial-least-squares discriminant analysis plots with glucose excluded demonstrated the remaining metabolites were still able to discriminate the groups. This study demonstrates that a panel of synovial metabolites can distinguish between septic and nonseptic equine SF, with glucose the principal discriminator.
Keywords: equine; metabolomics; nuclear magnetic resonance; osteoarthritis; osteochondrosis; sepsis; synovial fluid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mateos J.; Lourido L.; Fernandez-Puente P.; Calamia V.; Fernandez-Lopez C.; Oreiro N.; Ruiz-Romero C.; Blanco F. J. Differential Protein Profiling of Synovial Fluid from Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis Patients Using LC-MALDI TOF/TOF. J. Proteomics 2012, 75 (10), 2869–2878. 10.1016/j.jprot.2011.12.042. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sanchez Teran A. F.; Rubio-Martinez L. M.; Villarino N. F.; Sanz M. G. Effects of Repeated Intra-Articular Administration of Amikacin on Serum Amyloid A, Total Protein and Nucleated Cell Count in Synovial Fluid from Healthy Horses. Equine Vet. J. Suppl. 2012, 44 (43), 12–16. 10.1111/j.2042-3306.2012.00637.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

