Crystal structure of Escherichia coli purine nucleoside phosphorylase complexed with acyclovir
- PMID: 29969103
- PMCID: PMC6038453
- DOI: 10.1107/S2053230X18008087
Crystal structure of Escherichia coli purine nucleoside phosphorylase complexed with acyclovir
Abstract
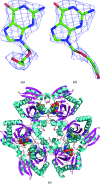
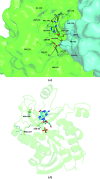
Escherichia coli purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP), which catalyzes the reversible phosphorolysis of purine ribonucleosides, belongs to the family I hexameric PNPs. Owing to their key role in the purine salvage pathway, PNPs are attractive targets for drug design against some pathogens. Acyclovir (ACV) is an acyclic derivative of the PNP substrate guanosine and is used as an antiviral drug for the treatment of some human viral infections. The crystalline complex of E. coli PNP with acyclovir was prepared by co-crystallization in microgravity using counter-diffusion through a gel layer in a capillary. The structure of the E. coli PNP-ACV complex was solved at 2.32 Å resolution using the molecular-replacement method. The ACV molecule is observed in two conformations and sulfate ions were located in both the nucleoside-binding and phosphate-binding pockets of the enzyme. A comparison with the complexes of other hexameric and trimeric PNPs with ACV shows the similarity in acyclovir binding by these enzymes.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; acyclovir; crystal structure; inhibitors; purine nucleoside phosphorylase; structure-based drug design; tumour-directed gene therapy.
Figures

References
-
- Bennett, E. M., Anand, R., Allan, P. W., Hassan, A. E. A., Hong, J. S., Levasseur, D. N., McPherson, D. T., Parker, W. B., Secrist, J. A., Sorscher, E. J., Townes, T. M., Waud, W. R. & Ealick, S. E. (2003). Chem. Biol. 10, 1173–1181. - PubMed
-
- Bennett, E. M., Li, C., Allan, P. W., Parker, W. B. & Ealick, S. E. (2003). J. Biol. Chem. 278, 47110–47118. - PubMed
-
- Bzowska, A., Ananiev, A. V., Ramzaeva, N., Alksins, E., Maurins, J. A., Kulikowska, E. & Shugar, D. (1994). Biochem. Pharmacol. 48, 937–947. - PubMed
-
- Caceres, R. A., Timmers, L. F. M. S., Ducati, R. G., da Silva, D. O. N., Basso, L. A., de Azevedo, W. F. Jr & Santos, D. S. (2012). Biochimie, 94, 155–165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

